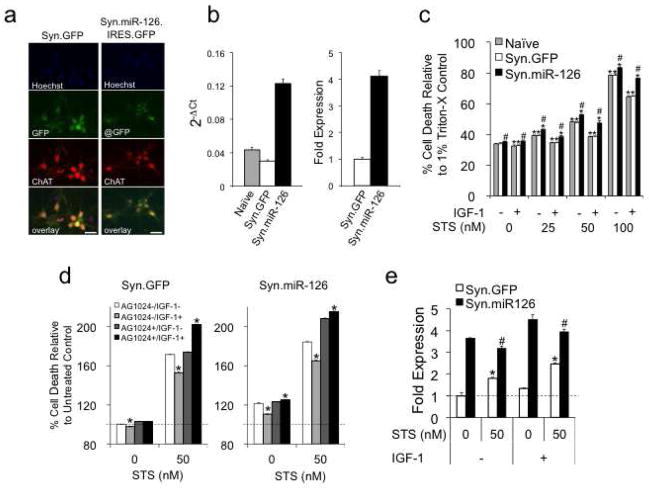
Fig. 1.
Overexpression of miR-126 increases STS toxicity and impairs a protective effect of IGF-1. (a, b) Transduction of cortical neurons with Syn.GFP control or Syn.miR-126.IRES.GFP (Syn.miR-126) revealed expression of GFP (a) and 4-fold upregulation of miR-126 (b). Neurons were immunostained for ChAT (red), and miR-126 expression was measured by qRT-PCR. Size bars = 20 μm. (c) LDH assays demonstrate an increase of STS toxicity and a reduction of neuroprotection by IGF-1 in miR-126 transduced cortical neurons. Data are plotted as relative cell death to Triton X (1%) induced maximum cell death. *: p < 0.05 comparing treated to untreated condition. #: p < 0.05 comparing miR-126 to Syn.GFP control. (d) The effects of IGF-1 can be inhibited by AG1024 (0.5 μM). Data are plotted as percent cell death relative to untreated Syn.GFP control. *: p < 0.05 comparing IGF-1 treated to IGF-1 untreated condition. (e) Expression levels of endogenous and virus-expressed miR-126 in STS and IGF-1 treated neurons. *: p < 0.05 comparing Syn.GFP to untreated condition. #: p < 0.05 comparing Syn.miR-126 to untreated condition.