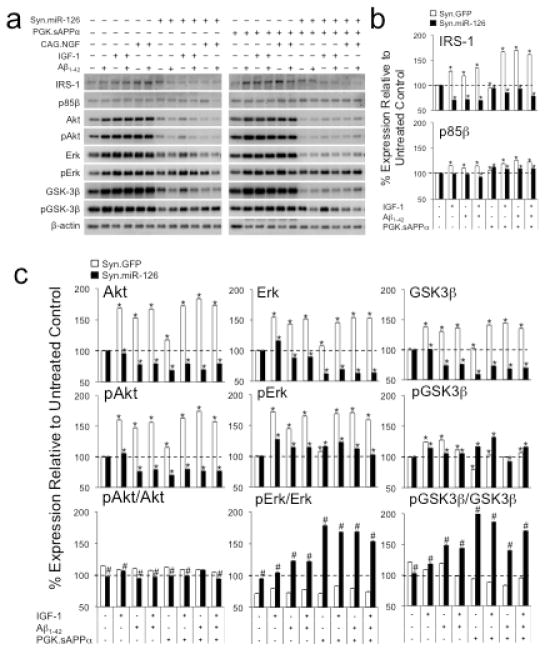
Fig. 6.
Overexpression of miR-126 modulates AKT/GSK-3β and ERK signaling in Aβ1-42, IGF-1 and sAPPα treated neurons. Quantification of Western blots (a) shows that IRS-1 is upregulated in Aβ1-42 and IGF-1 or sAPPα treated neurons, but downregulated when miR-126 is overexpressed (b). Expression levels of p85β are also increased in controls, but to lesser extent in miR-126 transduced cells. (c) Aβ1-42 and IGF-1 or sAPPα treatment cause upregulation of AKT, pAKT, ERK, pERK, GSK-3β, and to a lesser extent pGSK-3β in control cells. In contrast, except for pERK and pGSK-3β, miR-126 overexpressing neurons show downregulation of these molecules. While the pAKT/AKT ratios are unchanged and the pERK/ERK and pGSK-3β/GSK-3β ratios are reduced in the controls, miR-126 overexpressing cells have reduced pAKT/AKT and markedly increased pERK/ERK and pGSK-3β/GSK-3β ratios. In the miR-126 overexpressing cells sAPPα alone or in combination with IGF-1 increases the pERK/ERK and pGSK-3β/GSK-3β ratios. *: p < 0.05 comparing treated to untreated condition. #: p < 0.05 comparing ratios for Syn.miR-126 to ratios of Syn.GFP controls.