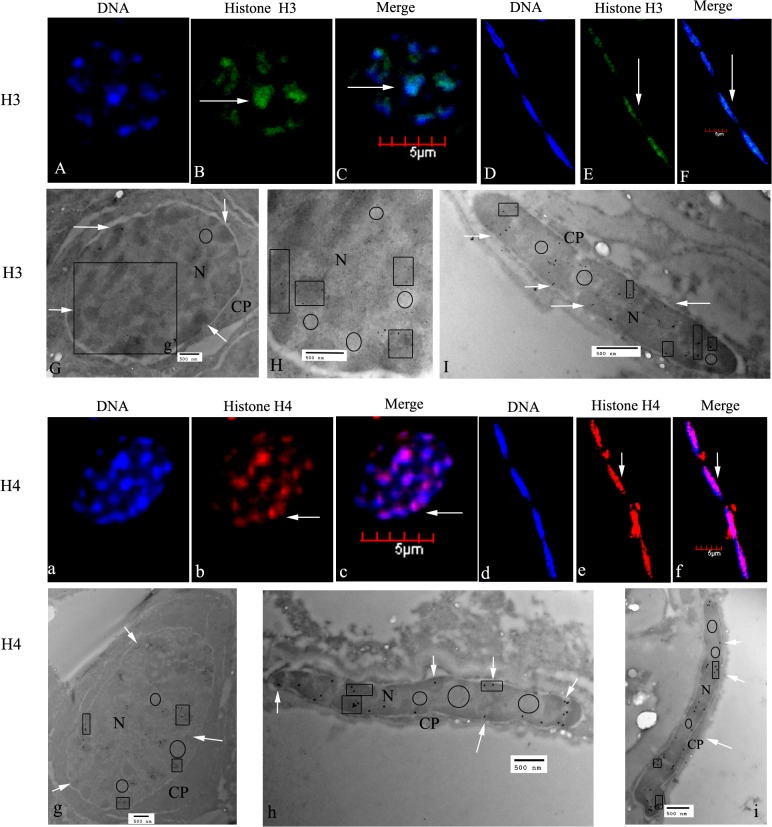
Fig 3. Localization of histones H3 and H4 in spermatogonia of E. sinensis.
(A–C) Immunofluorescent localization of histone H3 in spermatogonia. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue), and histone H3 was visualized with a goat polyclonal secondary antibody to rabbit IgG-Fc conjugated to DyLight 488 (green). (D–F) Immunofluorescent localization of histone H3 in testicular somatic cells. The nuclei show histone H3 staining (see arrows in E, F). (G) Ultrastructural localization of histone H3. Histone H3 was mainly localized in the nuclei of spermatogonia (see arrows in G). (H) A magnified part of G (g’); H3 was mainly localized in heterochromatin (see panes). (I) Ultrastructural localization of histone H3 in testicular somatic cells. H3 was mainly found in nuclear heterochromatin (see arrows and panes). (a–c) Immunofluorescent localization of histone H4 in spermatogonia. H4 was mainly localized in the nucleus (see arrows in b and c). (d–f) Immunofluorescent localization of histone H4 in testicular somatic cells. H4 was mainly found in nucleus (see arrows in e and f). (g) Ultrastructural localization of histone H4 by electron microscopy (EM). H4 was mainly found in the nuclear heterochromatin (see arrows and panes). (h and i) Ultrastructural localization of histone H4 in testicular somatic cells. H4 was mainly distributed in nuclear heterochromatin (see arrows and panes). Key: N, nucleus; CP, cytoplasm. The regions in panes represent heterochromatin, which stains intensely, the circled areas represent euchromatin, which is less intensely stained. Scale bars in immunofluorescent images = 5 μm; those within EM images = 500 nm.