Figure 1.
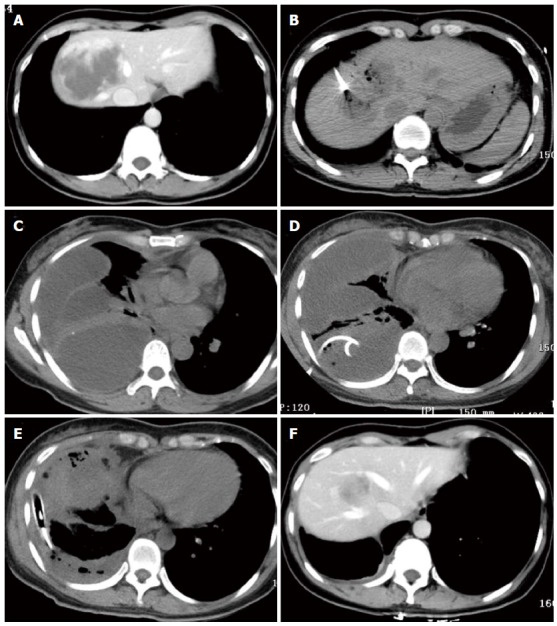
One patient with a 7.5-cm hemangioma mainly in segment 8 in the computed tomography-guided ablation group developed a diaphragmatic rupture after ablation. A: A 40-year-old woman in the computed tomography (CT)-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation group had a 7.5-cm hemangioma in segment 8, as illustrated on an abdominal CT scan; B: During CT-guided ablation, the lesion became depressed and commenced outgassing; C: Four days after ablation, CT scan of the chest showed a multiloculated pleural effusion occupying the right hemithorax with collapse of the right lung; D: Drainage via a chest tube was unsuccessful. She subsequently underwent thoracotomy; E: Two chest tubes were inserted into the pleural space; F: At 6 mo after ablation, CT scans showed that the hemangioma was completely ablated and markedly smaller without development of a diaphragmatic hernia.
