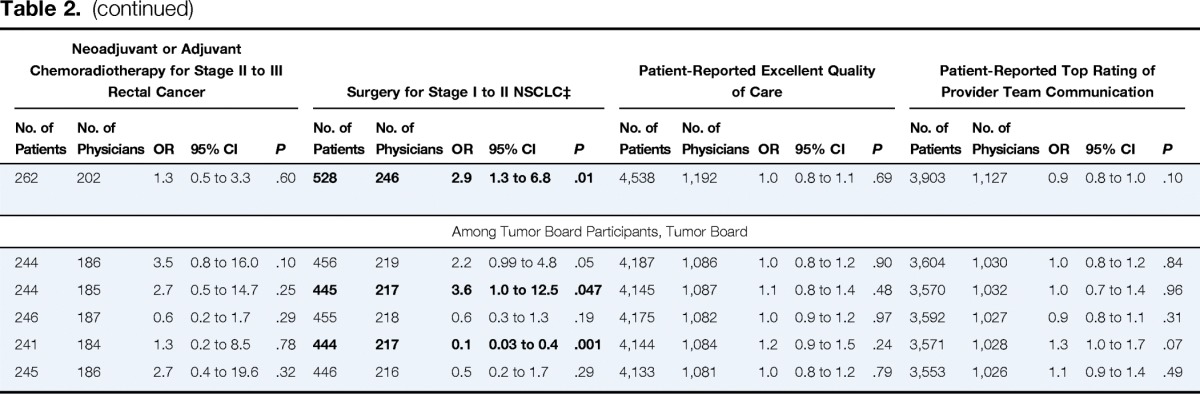
Table 2.
Associations Between Tumor Board Features and Patient Outcomes, Care Processes, and Ratings of Care*
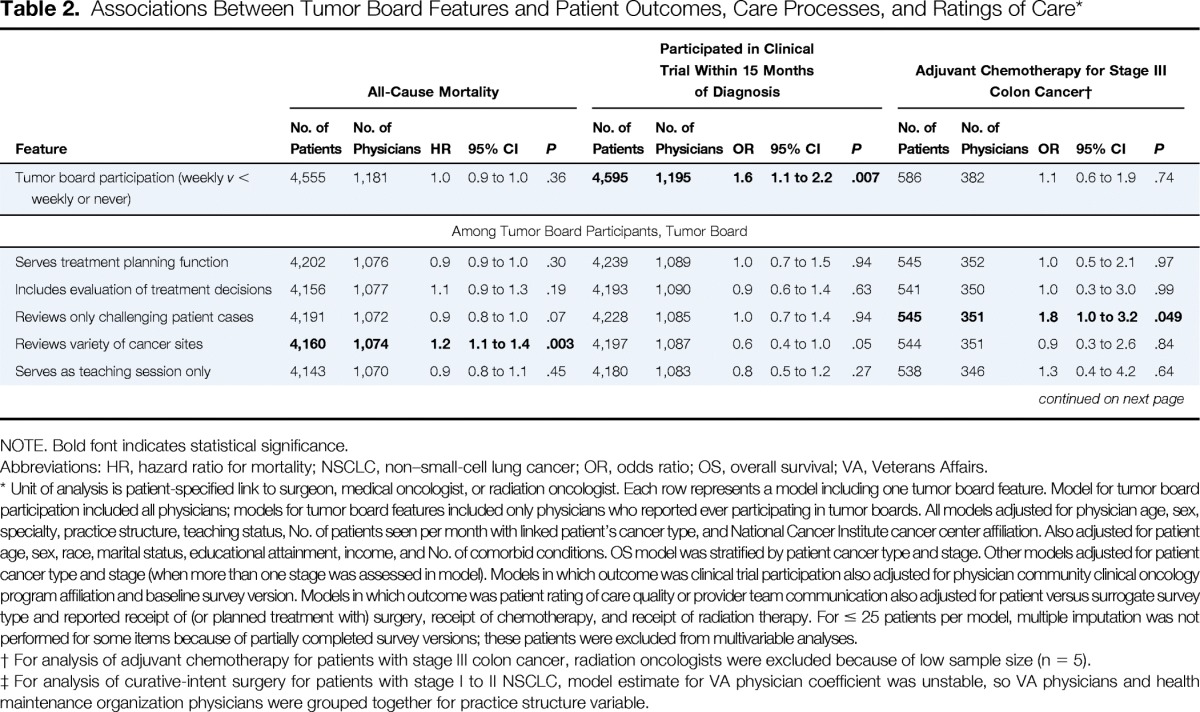
| Feature | All-Cause Mortality |
Participated in Clinical Trial Within 15 Months of Diagnosis |
Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Stage III Colon Cancer† |
Neoadjuvant or Adjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Stage II to III Rectal Cancer |
Surgery for Stage I to II NSCLC‡ |
Patient-Reported Excellent Quality of Care |
Patient-Reported Top Rating of Provider Team Communication |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | HR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | No. of Patients | No. of Physicians | OR | 95% CI | P | |
| Tumor board participation (weekly v < weekly or never) | 4,555 | 1,181 | 1.0 | 0.9 to 1.0 | .36 | 4,595 | 1,195 | 1.6 | 1.1 to 2.2 | .007 | 586 | 382 | 1.1 | 0.6 to 1.9 | .74 | 262 | 202 | 1.3 | 0.5 to 3.3 | .60 | 528 | 246 | 2.9 | 1.3 to 6.8 | .01 | 4,538 | 1,192 | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.1 | .69 | 3,903 | 1,127 | 0.9 | 0.8 to 1.0 | .10 |
| Among Tumor Board Participants, Tumor Board | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves treatment planning function | 4,202 | 1,076 | 0.9 | 0.9 to 1.0 | .30 | 4,239 | 1,089 | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.5 | .94 | 545 | 352 | 1.0 | 0.5 to 2.1 | .97 | 244 | 186 | 3.5 | 0.8 to 16.0 | .10 | 456 | 219 | 2.2 | 0.99 to 4.8 | .05 | 4,187 | 1,086 | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.2 | .90 | 3,604 | 1,030 | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.2 | .84 |
| Includes evaluation of treatment decisions | 4,156 | 1,077 | 1.1 | 0.9 to 1.3 | .19 | 4,193 | 1,090 | 0.9 | 0.6 to 1.4 | .63 | 541 | 350 | 1.0 | 0.3 to 3.0 | .99 | 244 | 185 | 2.7 | 0.5 to 14.7 | .25 | 445 | 217 | 3.6 | 1.0 to 12.5 | .047 | 4,145 | 1,087 | 1.1 | 0.8 to 1.4 | .48 | 3,570 | 1,032 | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.4 | .96 |
| Reviews only challenging patient cases | 4,191 | 1,072 | 0.9 | 0.8 to 1.0 | .07 | 4,228 | 1,085 | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.4 | .94 | 545 | 351 | 1.8 | 1.0 to 3.2 | .049 | 246 | 187 | 0.6 | 0.2 to 1.7 | .29 | 455 | 218 | 0.6 | 0.3 to 1.3 | .19 | 4,175 | 1,082 | 1.0 | 0.9 to 1.2 | .97 | 3,592 | 1,027 | 0.9 | 0.8 to 1.1 | .31 |
| Reviews variety of cancer sites | 4,160 | 1,074 | 1.2 | 1.1 to 1.4 | .003 | 4,197 | 1,087 | 0.6 | 0.4 to 1.0 | .05 | 544 | 351 | 0.9 | 0.3 to 2.6 | .84 | 241 | 184 | 1.3 | 0.2 to 8.5 | .78 | 444 | 217 | 0.1 | 0.03 to 0.4 | .001 | 4,144 | 1,084 | 1.2 | 0.9 to 1.5 | .24 | 3,571 | 1,028 | 1.3 | 1.0 to 1.7 | .07 |
| Serves as teaching session only | 4,143 | 1,070 | 0.9 | 0.8 to 1.1 | .45 | 4,180 | 1,083 | 0.8 | 0.5 to 1.2 | .27 | 538 | 346 | 1.3 | 0.4 to 4.2 | .64 | 245 | 186 | 2.7 | 0.4 to 19.6 | .32 | 446 | 216 | 0.5 | 0.2 to 1.7 | .29 | 4,133 | 1,081 | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.2 | .79 | 3,553 | 1,026 | 1.1 | 0.9 to 1.4 | .49 |
NOTE. Bold font indicates statistical significance.
Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio for mortality; NSCLC, non–small-cell lung cancer; OR, odds ratio; OS, overall survival; VA, Veterans Affairs.
Unit of analysis is patient-specified link to surgeon, medical oncologist, or radiation oncologist. Each row represents a model including one tumor board feature. Model for tumor board participation included all physicians; models for tumor board features included only physicians who reported ever participating in tumor boards. All models adjusted for physician age, sex, specialty, practice structure, teaching status, No. of patients seen per month with linked patient's cancer type, and National Cancer Institute cancer center affiliation. Also adjusted for patient age, sex, race, marital status, educational attainment, income, and No. of comorbid conditions. OS model was stratified by patient cancer type and stage. Other models adjusted for patient cancer type and stage (when more than one stage was assessed in model). Models in which outcome was clinical trial participation also adjusted for physician community clinical oncology program affiliation and baseline survey version. Models in which outcome was patient rating of care quality or provider team communication also adjusted for patient versus surrogate survey type and reported receipt of (or planned treatment with) surgery, receipt of chemotherapy, and receipt of radiation therapy. For ≤ 25 patients per model, multiple imputation was not performed for some items because of partially completed survey versions; these patients were excluded from multivariable analyses.
For analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage III colon cancer, radiation oncologists were excluded because of low sample size (n = 5).
For analysis of curative-intent surgery for patients with stage I to II NSCLC, model estimate for VA physician coefficient was unstable, so VA physicians and health maintenance organization physicians were grouped together for practice structure variable.
