Table 2.
Themes and Representative Quotes of Participants' Goals for Implementation of Distress Screening
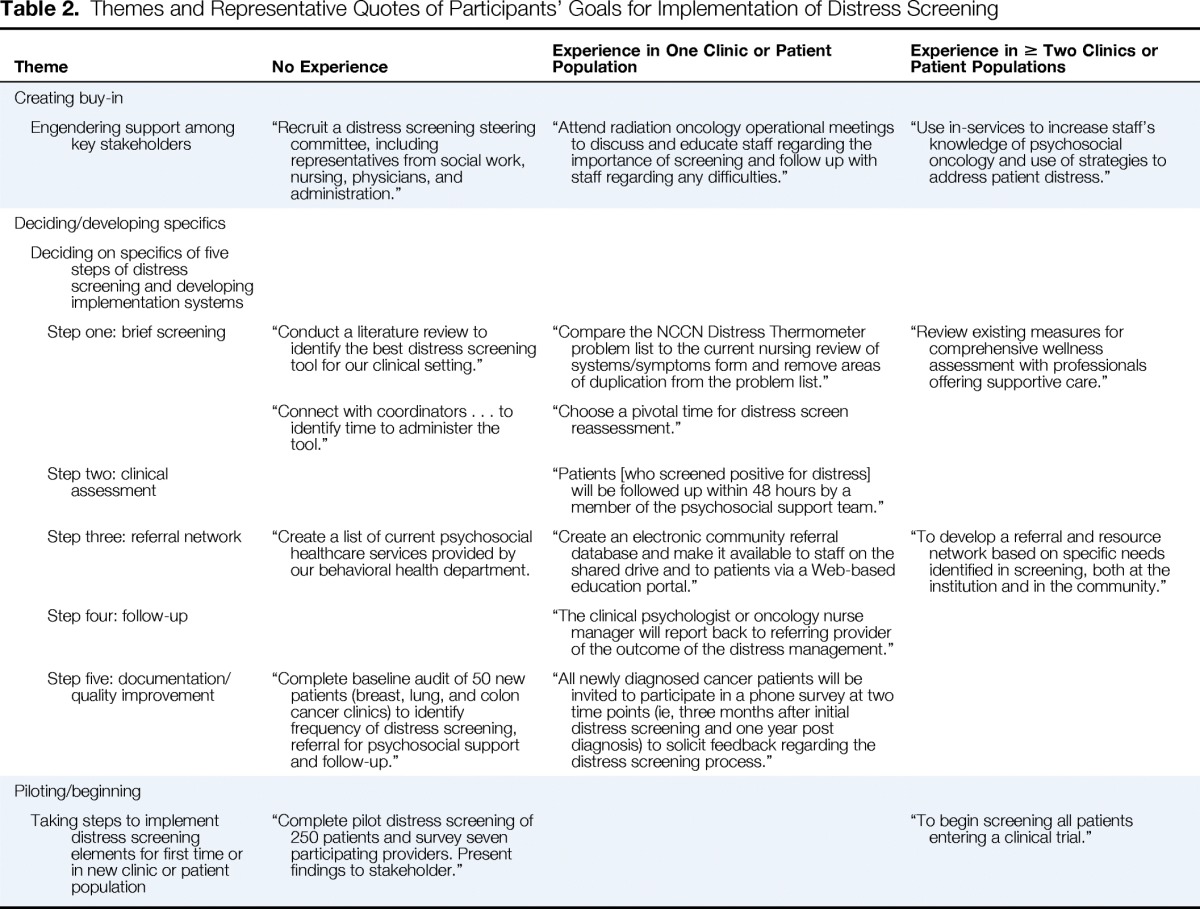
| Theme | No Experience | Experience in One Clinic or Patient Population | Experience in ≥ Two Clinics or Patient Populations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creating buy-in | |||
| Engendering support among key stakeholders | “Recruit a distress screening steering committee, including representatives from social work, nursing, physicians, and administration.” | “Attend radiation oncology operational meetings to discuss and educate staff regarding the importance of screening and follow up with staff regarding any difficulties.” | “Use in-services to increase staff's knowledge of psychosocial oncology and use of strategies to address patient distress.” |
| Deciding/developing specifics | |||
| Deciding on specifics of five steps of distress screening and developing implementation systems | |||
| Step one: brief screening | “Conduct a literature review to identify the best distress screening tool for our clinical setting.” | “Compare the NCCN Distress Thermometer problem list to the current nursing review of systems/symptoms form and remove areas of duplication from the problem list.” | “Review existing measures for comprehensive wellness assessment with professionals offering supportive care.” |
| “Connect with coordinators … to identify time to administer the tool.” | “Choose a pivotal time for distress screen reassessment.” | ||
| Step two: clinical assessment | “Patients [who screened positive for distress] will be followed up within 48 hours by a member of the psychosocial support team.” | ||
| Step three: referral network | “Create a list of current psychosocial healthcare services provided by our behavioral health department. | “Create an electronic community referral database and make it available to staff on the shared drive and to patients via a Web-based education portal.” | “To develop a referral and resource network based on specific needs identified in screening, both at the institution and in the community.” |
| Step four: follow-up | “The clinical psychologist or oncology nurse manager will report back to referring provider of the outcome of the distress management.” | ||
| Step five: documentation/quality improvement | “Complete baseline audit of 50 new patients (breast, lung, and colon cancer clinics) to identify frequency of distress screening, referral for psychosocial support and follow-up.” | “All newly diagnosed cancer patients will be invited to participate in a phone survey at two time points (ie, three months after initial distress screening and one year post diagnosis) to solicit feedback regarding the distress screening process.” | |
| Piloting/beginning | |||
| Taking steps to implement distress screening elements for first time or in new clinic or patient population | “Complete pilot distress screening of 250 patients and survey seven participating providers. Present findings to stakeholder.” | “To begin screening all patients entering a clinical trial.” |
