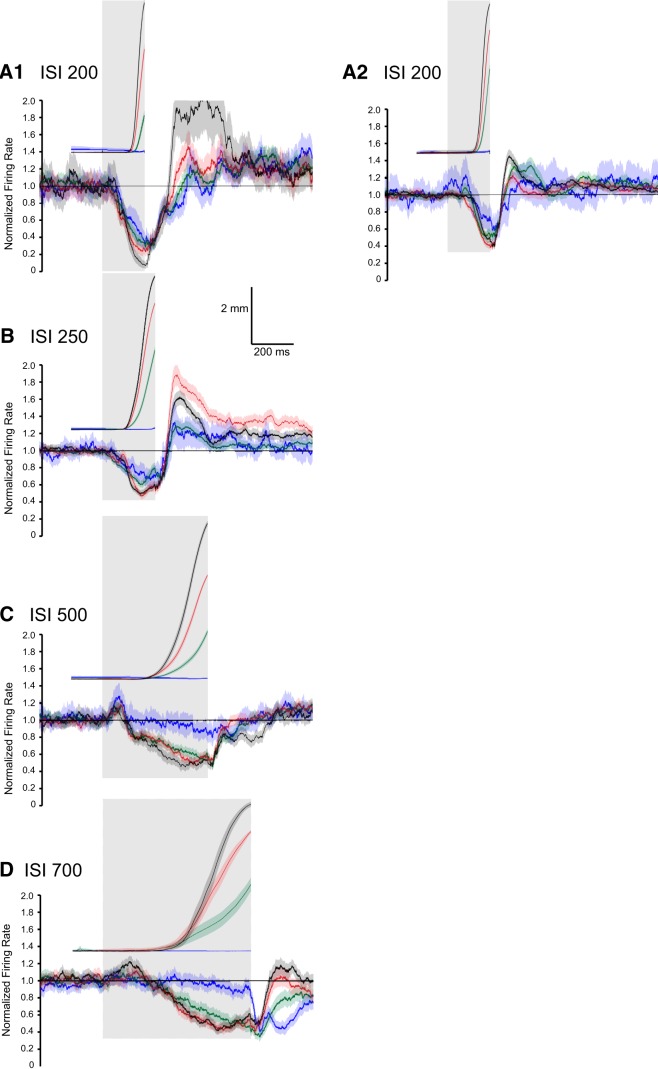
Figure 12.
Average activity of eyelid PCs and corresponding average eyelid responses (position), where trials are grouped by CR amplitude. For all panels the green traces represent the 33% of the trials with the smallest CR amplitudes, the black traces the 33% with the largest amplitudes, the red traces are the intermediate 33%, and the blue traces are the average of the non-CRs. A, Average activity of eyelid PCs and the corresponding eyelid CRs for those trials during training with an ISI of 200 ms. Results are plotted separately for two rabbits trained under that protocol. In both cases, there are differences in the average PC activity for trials with the highest CR amplitude versus non-CR trials. B, Same format for eyelid PCs recorded during training with an ISI of 250 ms. There are systematic differences in the PC activity for all four groups of CRs. Decreases were observed during the two shorter ISIs (200 and 250 ms) but were not sufficient to produce CRs. C, Same data format as above for the eyelid PCs recorded during training with an ISI 500 ms. D, Same format as above for the eyelid PCs recorded during training with an ISI 700 ms. For the two longer ISIs (500 and 700 ms) very small decreases in eyelid PC activity were observed during non-CR trials.