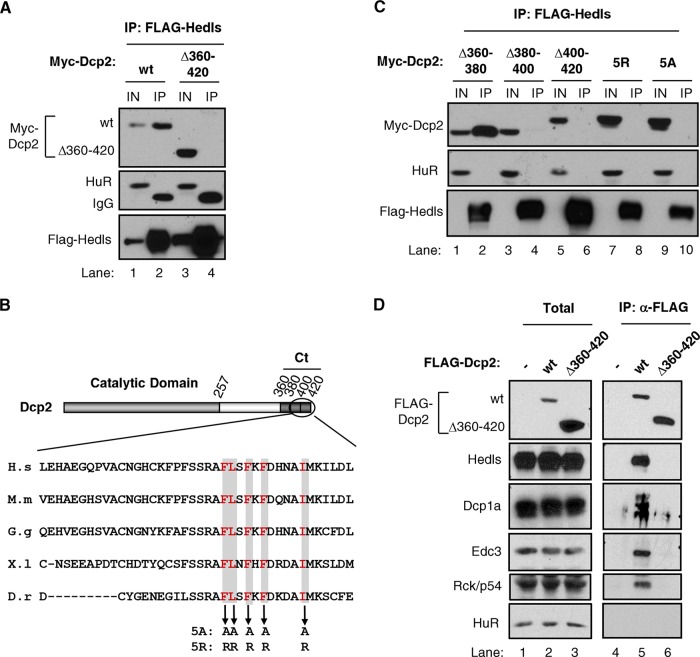
FIG 4.
The Dcp2 C terminus is required for Hedls interaction and decapping complex assembly. (A) Co-IP assays with RNase-treated lysates from HEK 293T cells transiently coexpressing Myc-tagged wild-type (wt) or mutant Dcp2 proteins, as indicated, with FLAG-tagged Hedls and immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-FLAG antibody. Total input samples (IN) were collected prior to immunoprecipitation. HuR served as a negative control. Mouse light-chain IgG was detected in the immunoprecipitated samples, as indicated. (B) Schematic of Dcp2 showing the catalytic region in light gray and the C-terminal (Ct) region in dark gray. Segments that were deleted are delineated with boxes. The Hedls interaction domain is shown, and the conserved hydrophobic residues that were mutated are shown in red and shaded. H.s, Homo sapiens; M.m, Mus musculus; G.g, Gallus gallus; X.l, Xenopus laevis; D.r, Danio rerio. (C) The same as panel A, but monitoring the indicated Dcp2 mutant proteins. (D) The same as panel A, but using HEK 293T T-REx cells stably expressing the indicated FLAG-tagged Dcp2 proteins and monitoring the copurification of endogenous proteins, as indicated. Total, 5% of total extract.