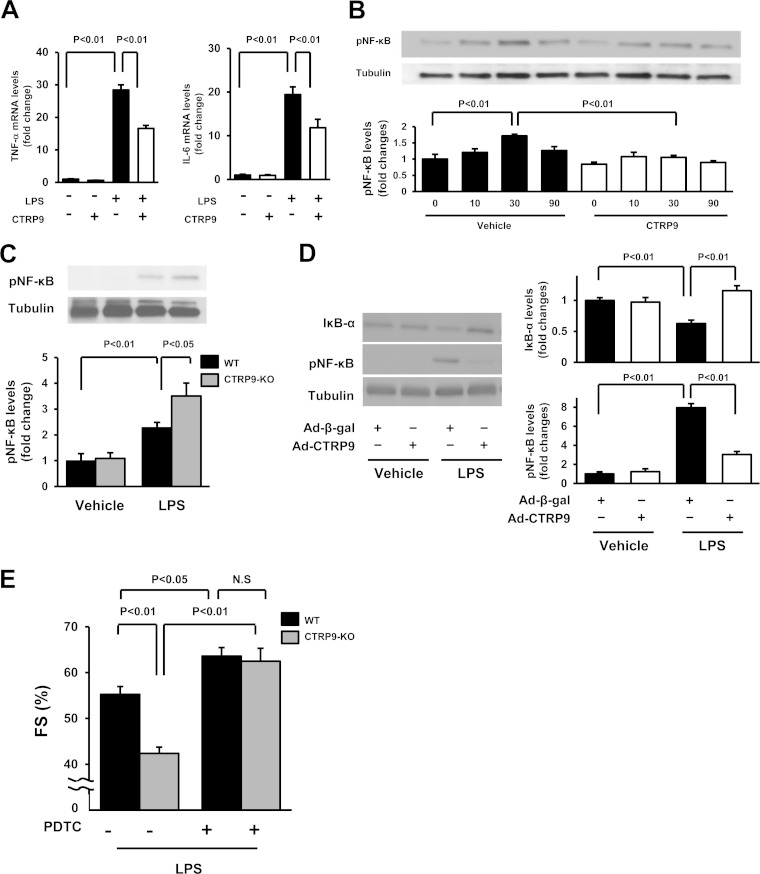
FIG 3.
CTRP9 suppresses the inflammatory response to LPS in cultured cardiac myocytes. (A) Effect of CTRP9 on LPS-induced expression of TNF-α (left) and IL-6 (right) in cardiac myocytes. Cells were pretreated with CTRP9 (10 μg/ml) or vehicle for 4 h and stimulated with or without LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 h. The mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-6 was measured by real-time PCR method and expressed relative to β-actin levels (n = 6). (B) Effect of CTRP9 on NF-κB phosphorylation in response to LPS. Cells were pretreated with CTRP9 (10 μg/ml) or vehicle for 4 h followed by stimulation with LPS (100 ng/ml) or vehicle for the indicated length of time (n = 3). Phosphorylation of NF-κB (pNF-κB) was determined by Western blotting. The phosphorylation level was determined by measuring the corresponding band intensities using ImageJ software, and the relative values were expressed relative to the α-tubulin signals. (C) Phosphorylation of NF-κB in the hearts of CTRP9-KO and WT mice at 6 h after injection of LPS or vehicle, as assessed by Western blotting. (D) NF-κB phosphorylation and IκB-α protein expression in the heart of mice treated with Ad-CTRP9 or Ad-β-gal at 6 h after LPS or vehicle injection. WT mice were systemically treated with Ad-CTRP9 or Ad-β-gal (3.0 × 108 PFU total) 5 days before LPS or vehicle injection. (E) Quantitative analysis of the %FS after treatment with the NF-κB inhibitor, PDTC, or vehicle in CTRP9-KO and WT mice at 6 h after LPS injection (n = 5 in each group). PDTC (100 mg/kg) or vehicle was given by intraperitoneal injection in CTRP9-KO and WT mice 1 h before LPS treatment. The results are presented as the means ± the SEM.