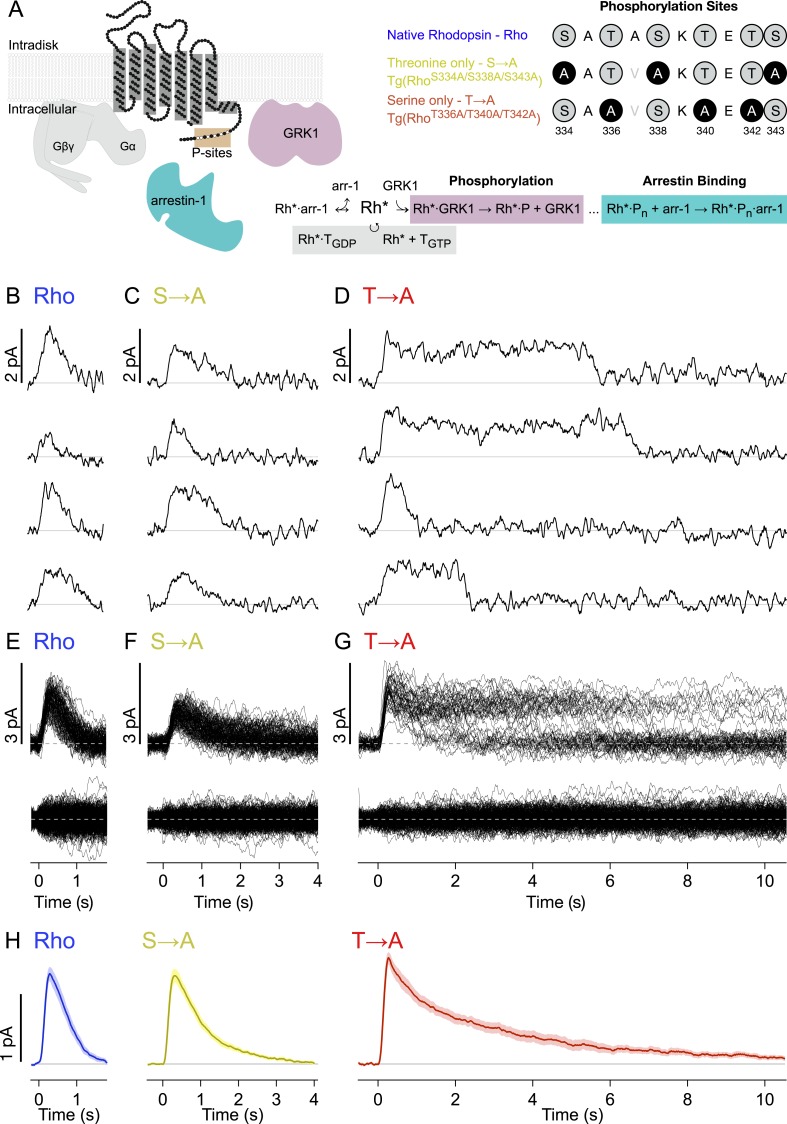
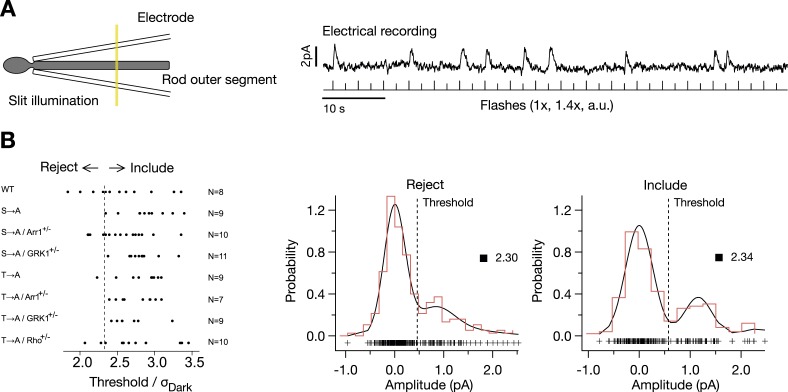
Figure 1. Single-photon responses: activation of individual wild-type and mutant rhodopsins.
(A) Schematic showing rhodopsin, the G protein transducin (T = Gβγ and Gα, gray), G protein receptor kinases 1(GRK1), and arrestin-1. Phosphorylation consists of GRK1 binding and phosphate attachment. Arrestin-1 serves to quench rhodopsin activity and to compete with GRK1, modifying the GRK1 binding rate (Doan et al., 2009). The upper right panel shows the sequence of the rhodopsin C-terminus and the mutations to test the effects of replacing either threonine or serine residues with alanine. The mutation A337V is included to produce a linear epitope for mAb 3A6, as in Mendez et al. (2000). Labels indicate strain nomenclature (above) and protein nomenclature (below). (B–D) Representative examples of individual single-photon responses (SPRs). (E–G) All SPRs from representative cells of each strain, with identified singles (∼50) above and failures (no response to flash, ∼150) below: (B, E) Rhodopsin (wild type, WT); (C, F) S → A, previously referred to as STM (Mendez et al., 2000); (D, G) T → A. (H) Average SPRs across all cells: WT—N = 8, S → A—N = 9, T → A—N = 9.