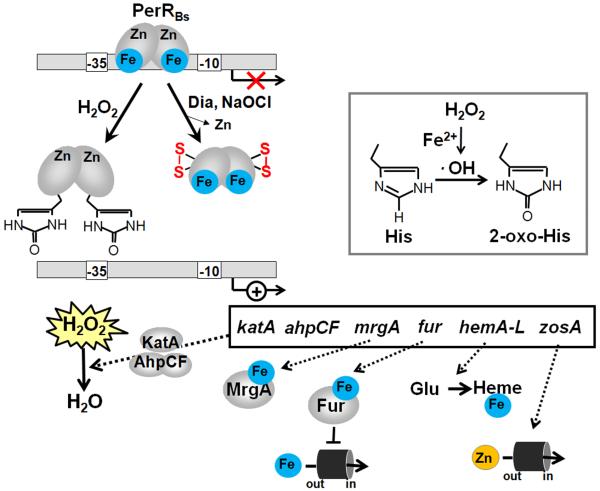
Figure 3. Redox-regulation of B. subtilis PerRBs by peroxides (metal-catalyzed histidine oxidation) and by diamide stress (intramolecular disulfides) and functions of the PerR regulon members.
PerR has a regulatory Fe2+or Mn2+-binding site with Asp and His residues as ligands and a structural Zn2+-binding site coordinated by four cysteine residues. Reaction of PerR-Fe with H2O2 leads to a Fenton reaction generating HO with subsequent oxidation of His37 and His91 to the 2-oxo-His derivatives that inactivate the PerR repressor under H2O2 stress leading to up-regulation of the PerR regulon genes. Under disulfide stress conditions provoked by diamide and NaOCl, PerR is inactivated by intramolecular disulfide formation in the Zn-binding site that also lead to derepression of the PerR regulon genes. The PerR regulon includes genes with antioxidant functions, such as the catalase and peroxiredoxin (katA, ahpCF), Fe-storage miniferritin (mrgA), ferric uptake regulator (fur), heme biosynthesis enzymes (hemAXCDBL) and zinc uptake systems (zosA). Examples for PerR regulon genes of B. subtilis and their functions are also listed in Table 2.