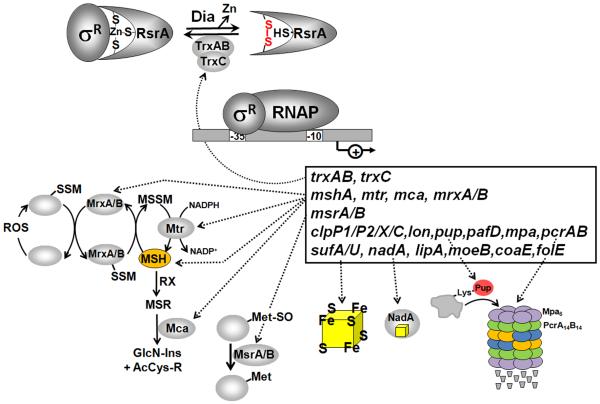
Figure 9. Redox regulation of the ZAS factor RsrA and its cognate sigma factor SigR in S. coelicolor and role of the SigR regulon.
RsrA is a redox-sensitive zinc-binding anti sigma (ZAS) factor in S. coelicolor that sequesters its cognate sigma factor SigR under reducing conditions. Diamide stress leads to intramolecular disulfide formation in RsrA, resulting in Zn release and relief of SigR. Free SigR activates transcription of the SigR regulon that functions to restore the thiol-redox balance. The SigR regulon includes genes for thioredoxins and thioredoxin reductase (trxAB, trxC), enzymes for mycothiol biosynthesis and recycling (mshA, mca, mtr), mycoredoxins (mrxA, mrxB), methionine sulfoxide reductase (msrA, msrB), protein quality control machinery (pepN, ssrA, clpP1P2, clpX, clpC, lon), ubiquitin-like protein-conjugation pathway and proteasomal components (pup, mpa, pafD, prcAB), Fe-S assembly components (sufA, sufU) and Fe-S containing enzymes (nadA, lipA), biosynthesis enzymes for the cofactors Fe-S, folate, CoASH and lipoic acid (moeB, coaE, folE, lipA). Examples for SigR regulon genes and their functions are also listed in Table 6.