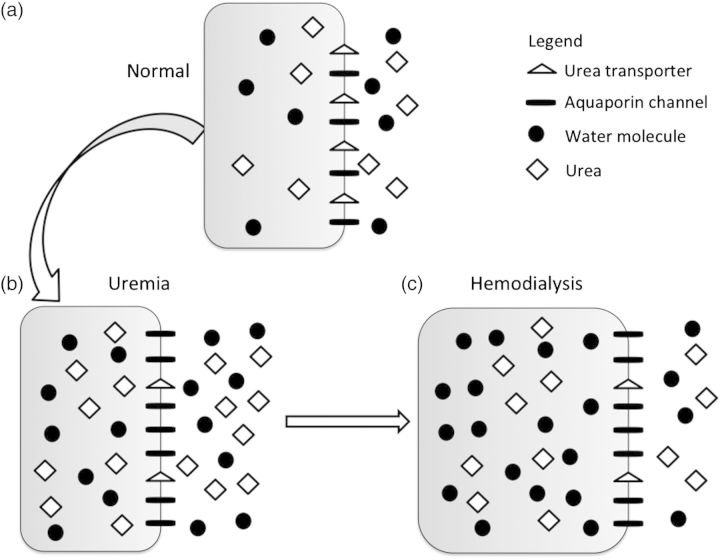
Fig. 1.
Changes in brain urea transporter (UT) and aquaporin channel (AQP) expression. (a) Normal, non-uremic milieu. (b) During chronic uremia, UT expression decreases by ∼50%, while that of AQP increases by ∼165% [6]. (c) During rapid urea removal, as occurs during HD, the reduced number of brain UT results in slower movement of urea from the intracellular to extracellular compartment, than is removed from the extracellular compartment by dialysis. The resulting osmotic gradient, coupled with increased brain AQP expression, results in water movement into cells, and subsequent cerebral edema.