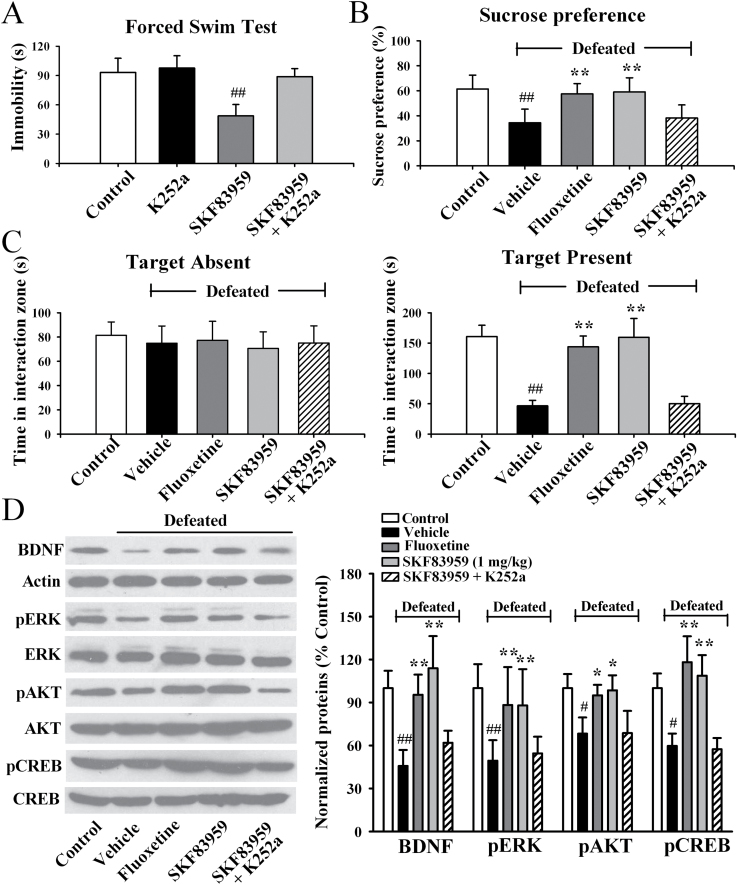
Figure 7.
Blockade of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) signaling by K252a abolishes the antidepressant actions of 6-Chloro- 7,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-1-(3-methylphenyl)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine (SKF83959). (A) Mice were first treated with K252a (5 nmol/mouse, daily) for 3 days, then administrated with SKF83959 (1mg/kg, i.p.) and followed by examination of forced swim test (FST). K252a pretreatment dramatically prevented the SKF83959-induced decrease of immobility in the FST (n=10). (B) Chronic social defeat stress (CSDS)-treated mice were co-injected with SKF83959 and K252a for 14 days; behavioral tests were then performed. SKF83959+K252a mice displayed lower sucrose preference than SKF83959-treated mice (n=10). (C) Co-treatment SKF83959 with K252a blocked the antidepressant effects of SKF83959 in the social interaction test (n=10). (D) K252a injection antagonized the actions of SKF83959 on hippocampal BDNF, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK), Protein Kinase B (pAKT), and cAMP response element-binding protein (pCREB) of chronic social defeat stress (CSDS)-treated mice (n=5). Data are expressed as means±SEM; # P <.05, ## P <.01 vs control; * P < .05, ** P <.01 vs defeated + vehicle group. Comparison was made by 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by posthoc Bonferroni’s test.