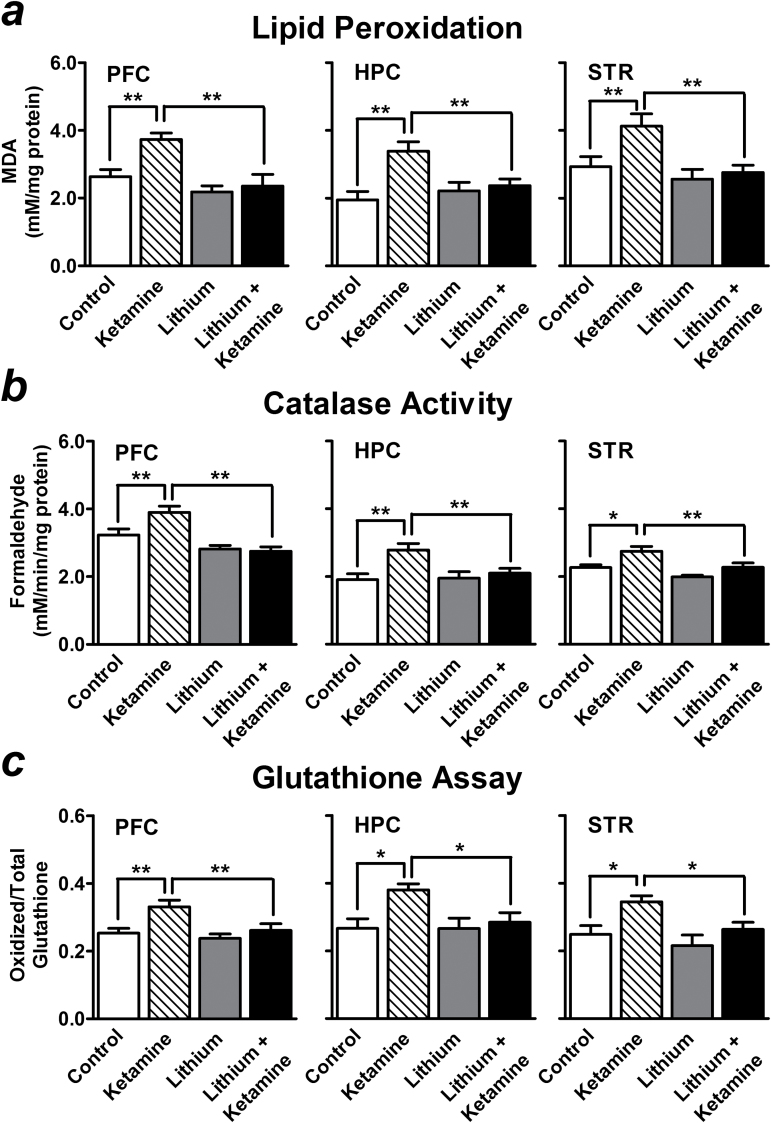
Figure 4.
Preketamine treatment with a low therapeutic dose of lithium suppresses acute ketamine-induced oxidative stress. Acute ketamine injection at a dose that produces antidepressant-like effect (50mg/kg) markedly increased lipid peroxidation (a), catalase activity (b), and the levels of oxidized glutathione (c) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus (HPC), and striatum (STR) of stressed mice 20 minutes after injection. Compared with control stressed mice, preketamine treatment with 1200mg/L of lithium for 3 weeks robustly suppressed the oxidative metabolism markers induced by acute ketamine (lithium + ketamine group) in these brain regions. Data are mean±SEM (n =6–10). *P<.05, **P<.01, according to Student–Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test after a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).