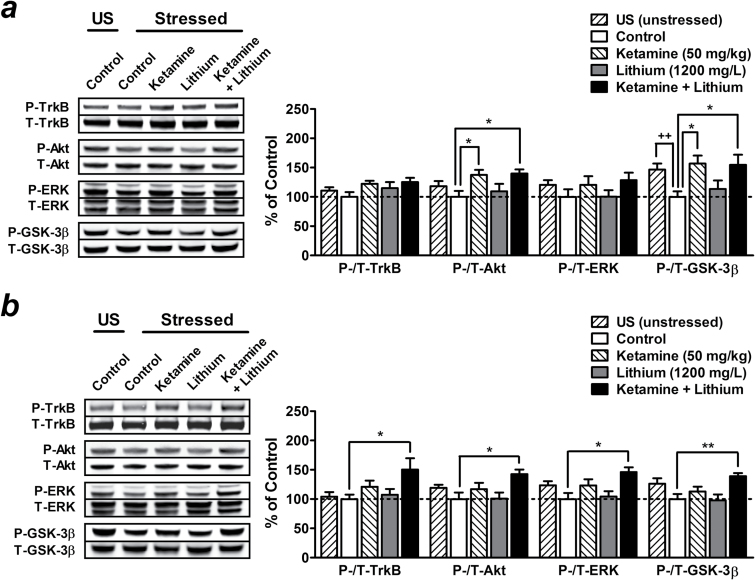
Figure 7.
Postketamine treatment with a low therapeutic dose of lithium maintains the inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and activation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) signaling pathway induced by a single injection of ketamine. Stressed mice received long-term treatment with 1200mg/L of lithium in drinking water immediately after a single injection of saline (lithium alone group) or 50mg/kg of ketamine (ketamine + lithium group), and brain tissues were collected after 1 (a) or 2 weeks (b) of lithium treatment. Typical Western blots and quantified results are shown. Phosphorylation levels of TrkB, Akt, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and GSK-3β in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) were normalized to the levels of total protein and expressed as percentage of control group. Data are mean±SEM (n =6–8). ++P<.01, t test; *P<.05, **P<.01, according to Student–Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test after a 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P, phosphorylated protein; T, total protein; US, unstressed.