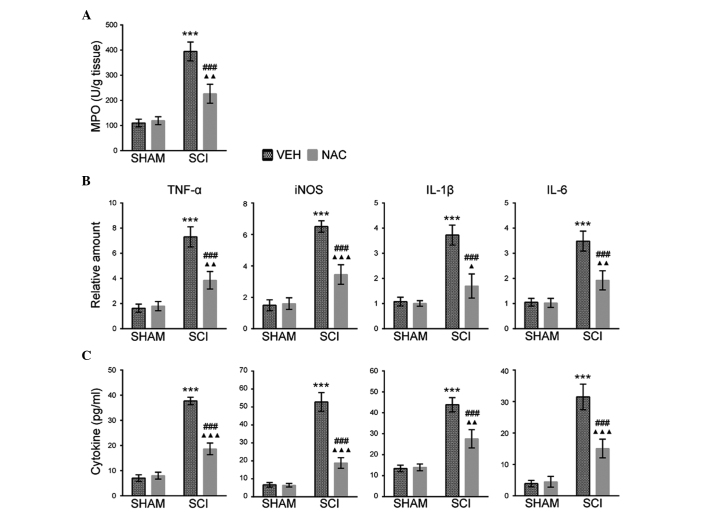
Figure 4.
Effects of NAC on MPO activity and inflammatory mediator expression. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments (n=3 per group). ***P<0.001, SCI+VEH mice versus SHAM+VEH mice; ###P<0.001, SCI+NAC mice versus SCI+VEH mice; ΔP<0.05, ΔΔP<0.01, ΔΔΔP<0.001, SCI+NAC mice versus SHAM+NAC mice. (A) MPO activity as an indicator of leukocyte infiltration was analyzed at 24 h in SHAM and SCI mice treated with NAC or VEH. (B) Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction of TNF-α, IL-1β (at 2 h), IL-6 and iNOS (at 6 h) was performed in SHAM and SCI mice treated with NAC or VEH. (C) ELISA of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and iNOS was performed at 24 h in SHAM and SCI mice treated with NAC or VEH. NAC, N-acetylcysteine; VEH, vehicle; SCI, spinal cord injury; RCR, respiratory control ratio; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin; MPO, myeloperoxidase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.