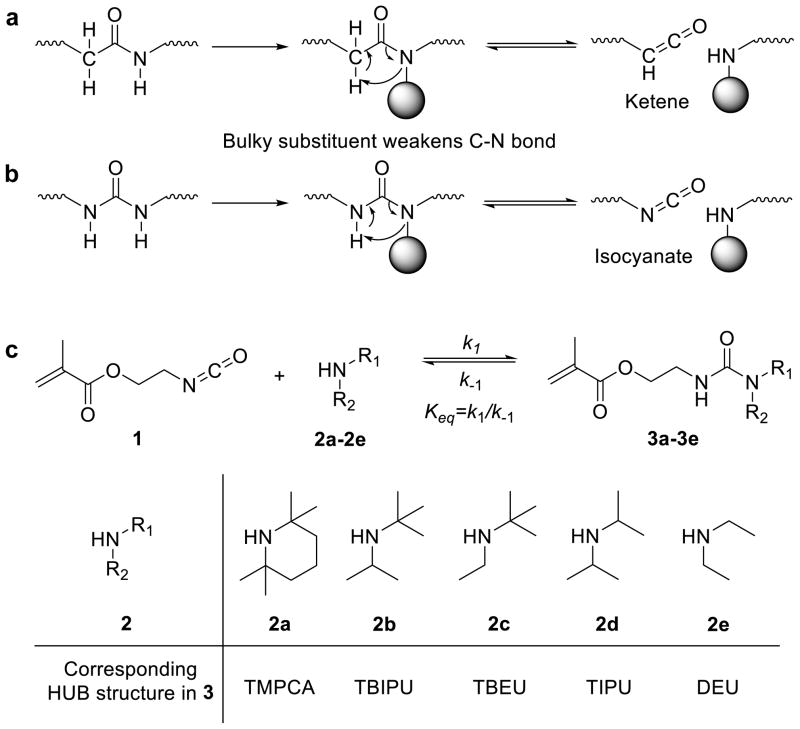
Figure 1. Dissociation of carboxylate/amine bonds bearing bulky N-substituent.
(a) Hindered amide bond dissociates to unstable ketene intermediate. (b) Hindered urea bond (HUB) dissociates to isocyanate, which is stable at low temperature but reactive to amine to reform the HUB bond, making HUB a dynamic covalent bond; (c) Equilibrium between isocyanate 1, bulky amines (2a–e) and corresponding ureas (3a–e), the chemical structures of bulky amines (2a–e), and the urea 3a–e bearing the corresponding HUB: 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinylcarboxyamide (TMPCA), N-tertbutyl-N-isopropylurea (TBIPU), N-tertbutyl-N-ethylurea (TBEU), N,N-diisopropylurea (DIPU) and N,N-diethylurea (DEU).