Fig 4. Scheme for dual action of casein kinase 1 (Hhp) on cohesin subunits to regulate meiotic chromosome segregation via Rec8 phosphorylation and to promote linear element formation, meiotic DSB formation, and recombination via Rec11 phosphorylation.
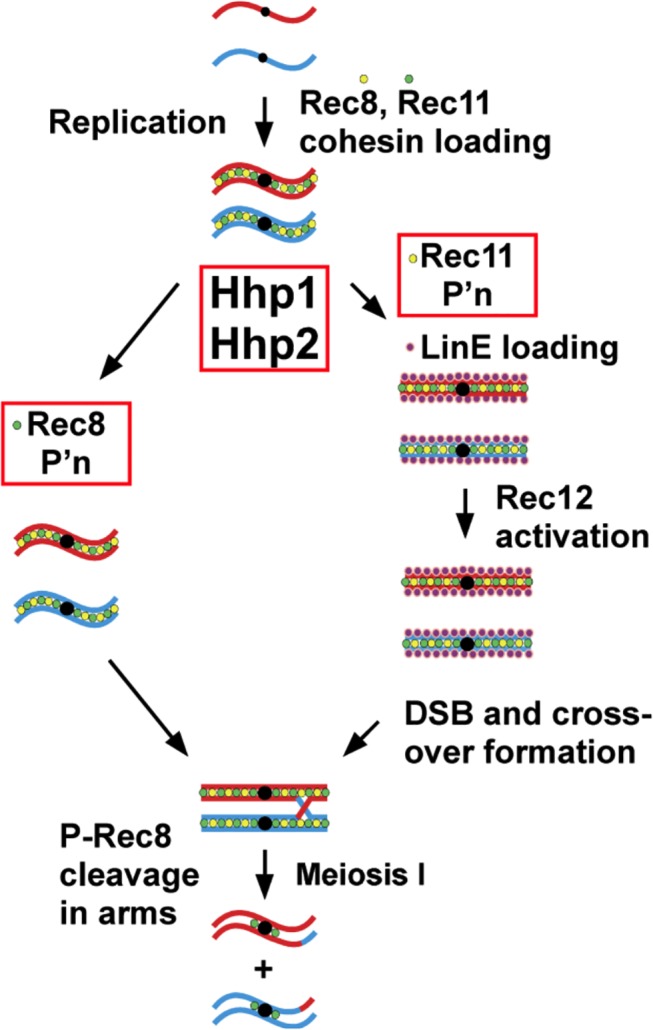
Cohesin subunits Rec8 and Rec11 are loaded onto chromosomes prior to premeiotic replication, during which sister chromatid cohesion is established. Before, during, or after loading they are phosphorylated by casein kinase homologs Hhp1 and Hhp2. Right: Phosphorylation (P’n) of Rec11 leads to loading of the linear element (LinE) proteins Rec10, Rec25, Rec27, and Mug20, which in turn activate Rec12 (Spo11 homolog) and its partner proteins for DSB formation; DSBs lead to crossovers, which allow segregation of homologous centromeres, not sister centromeres, at the first meiotic division (MI). Left: Phosphorylation of Rec8 (generating P-Rec8) allows its cleavage, first in the arms, which allows segregation of homologous centromeres at MI; later, cleavage of Rec8 in the centromeres allows segregation of sister centromeres at MII. Rec8 is also needed for loading of Rec11 (S10 Fig) [42] and is thus indirectly required for DSB formation and recombination [14,18]. The precise timing of Rec8 and Rec11 phosphorylation is unknown. Rec8 and Rec11 (STAG3 functional homolog) and their phosphorylation may play similar roles in mammalian gametogenesis (see Discussion).
