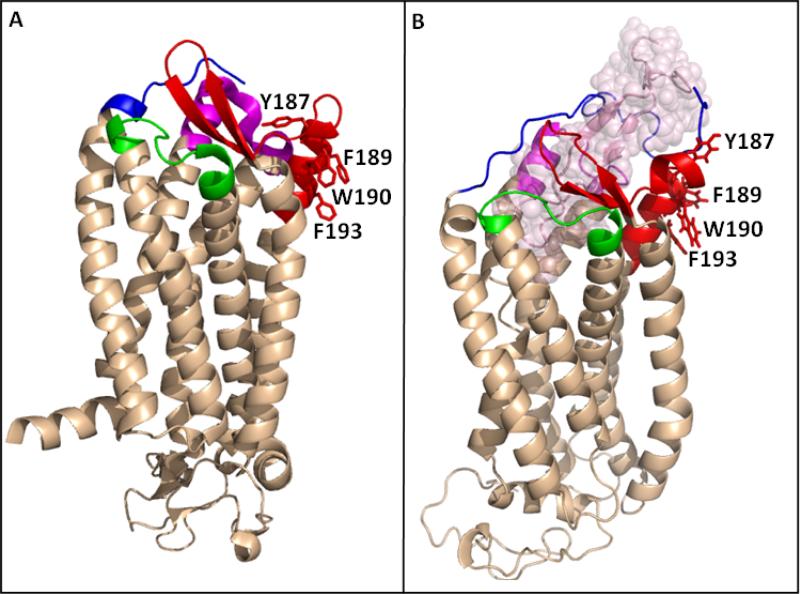
Fig. 9.
The orientation of the side chains of Y187, F189, W190 and F193 in the crystal structure of CCR5. (A) Structure of the CCR5 chemokine receptor-HIV entry inhibitor maraviroc complex (Tan, Q. et al. (2013) Structure of the CCR5 chemokine receptor-HIV entry inhibitor maraviroc complex, Science 341, 1387-1390.). The CCR5 N-terminus (residues 20-27) is colored in blue. ECL1 (90AAAQWDFGNTM101C) is presented in green, ECL2 region, residues R168-K197, is colored in red and ECL3 (260FQEFFGLNNCSSSNRL276D) is presented in magenta. (B) A model of CCR5 in complex with gp120 V3 region (Tamamis & Floudas (2014) Molecular Recognition of CCR5 by an HIV-1 gp120 V3 Loop, PlosOne 9, e95767). Color code as in (A), with the V3 region presented in light-pink spheres. F189, W190 and F193 are presented in sticks in (A) and (B) revealing that in the crystal structure these hydrophobic amino acids point away from the receptor binding pocket and towards the putative location of the cell membrane.