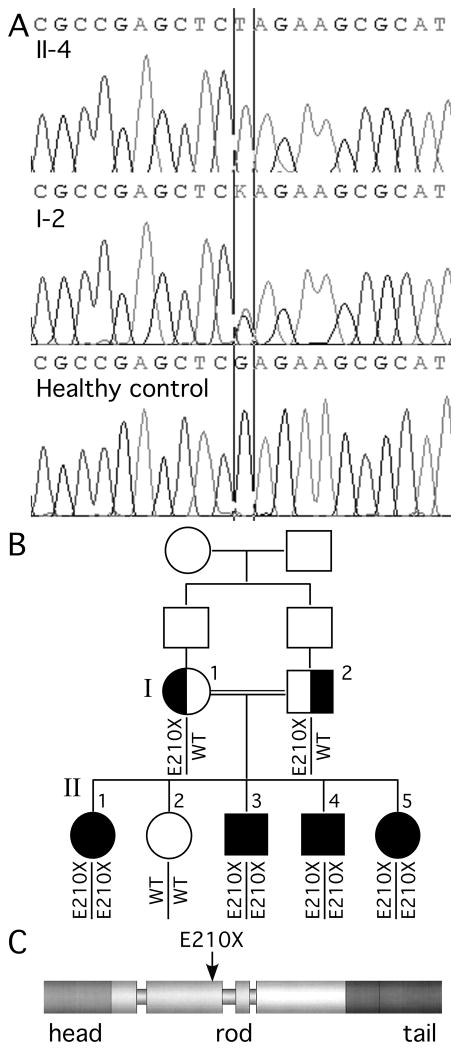
Fig. 1. Family pedigree and mutational analysis.
Panel A shows the electrophoretograms of the DNA sequence harboring the c.628G>T mutation for individuals II-4 and I-2 as well as a healthy control (the color versions are shown in Supplemental Fig. 1). In panel B, note that the unaffected sister (II-2) does not have the mutation, all affected children (II-1, II-3, II-4, and II-5) are homozygous, and both parents (I-1 and I-2) are heterozygous for the mutation. The siblings of the parents are not shown, and their parents are not available for genetic testing. Panel C shows the predicted effect of the E210X mutation on the domain structure of the human NFL protein.