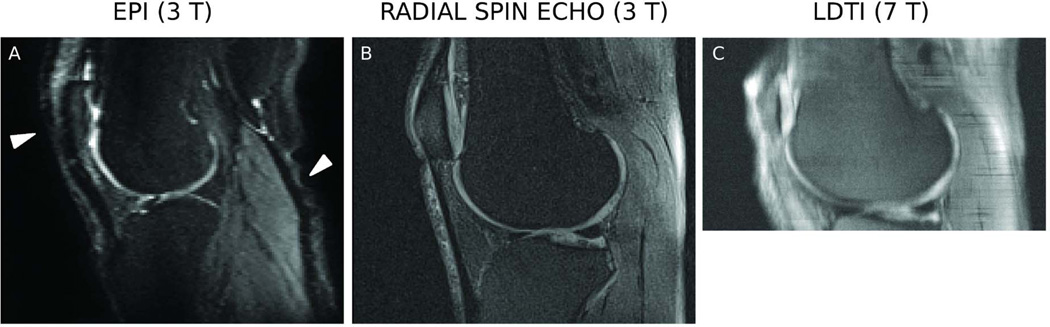
Figure 2.
Diffusion-weighted images acquired on a 39-years old asymptomatic male subject with different diffusion sequences. Clincal MRI of this subject (Sagittal and coronal PD and T1-weighted, not shown here) showed no signs of cartilage abnormality. A. Diffusion-weighted (b=400 s/mm2) images acquired with a DW-EPI sequence on a 3 T scanner (TE/TR = 56/5500 ms, slice thickness = 3 mm, 21 slices, field of view [FOV] = 176×176 mm2, in-plane resolution = 1.19×1.19 mm2, 6 averages, bandwidth = 1024 Hz/pixel, b-value = 0,400 s/mm2, phase samples = 123, parallel imagine acceleration factor (iPat) = 3, 36 reference lines, acquisition time = 2:34 min). Arrows in the EPI images indicate areas of geometric distortion. B. Diffusion-weighted images (b=350 s/mm2) acquired with a RAISED sequence on a 3 T scanner (TE/TR = 38/1500 ms, slice thickness = 3 mm, 21 slices, FOV = 154×154 mm2, in-plane resolution = 0.75×0.75 mm2, b-value = 0,350 s/mm2, bandwidth = 290 Hz/pixel, spokes = 114 [2.89 acceleration with respect to the Niquist condition], acquisition time = 2:50 min per b-value). C. Diffusion-weighted images acquired on a 7 T whole body scanner using a LSDTI sequence (TE/TR = 46/180 ms, slice thickness = 3 mm, 15 slices, FOV = 154×154 mm2, in-plane resolution = 0.6×0.6 mm2, b-value = 450 s/mm2, bandwidth = 500 Hz/pixel, rotation angle = 20°, acquisition time = 2:48 min per slice and 7 diffusion weightings).