Fig. 2. The B-subunits of LT-I and LT-IIa enterotoxins induced cell clustering of B and T cells.
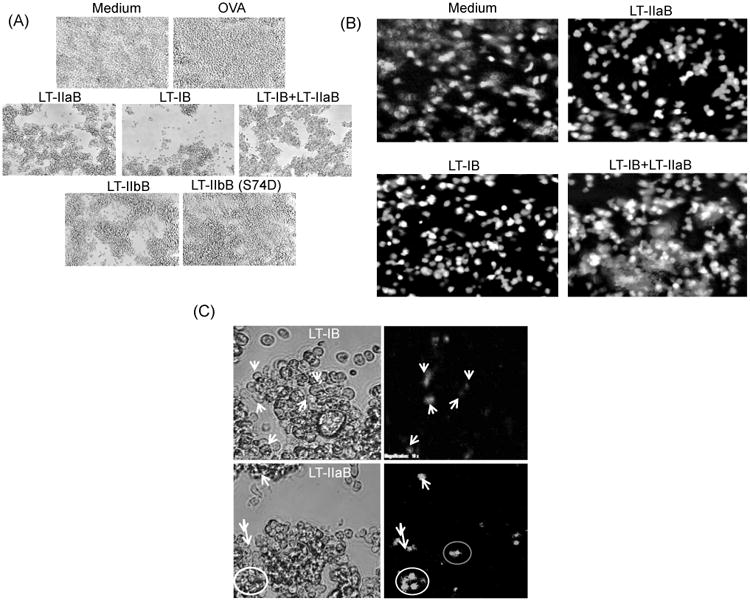
A20 WT B cells were cultured with or without OVA in presence of 20 μg/ml LT-IB, 10 μg/ml LT-IIaB, same doses of LT-IB+LT-IIaB, 10 μg/ml LT-IIbB or 10 μg/ml non-TLR-2 binding mutant of LT-IIbB, LT-IIbB(S74D), for 4-6 hrs. Unlabelled OVA-specific DO.11.10 T cells were added to the culture, and incubated for 24 hrs (A). Alternatively, A20 WT B cells were incubated for 4-6 hrs with lower doses of 5 μg/ml LT-IB, 2.5 μg/ml LT-IIaB, and same doses of LT-IB+LT-IIaB (B). CFSE-labeled T cells were then added and examined either after 2 hrs (B) or 24 hrs (C). Cells were examined by fluorescence microscopy [×20 (A and B), 10× cropped images (C)]. In (C), white arrows point to cells from same images taken in bright and overlapping fluorescence fields. Shown are cells incubated with the B-subunits without OVA. Almost identical cellular profile was found after cells were incubated in the presence of OVA (not shown). The data are representative of at least 2 similar experiments.
