Figure 1.
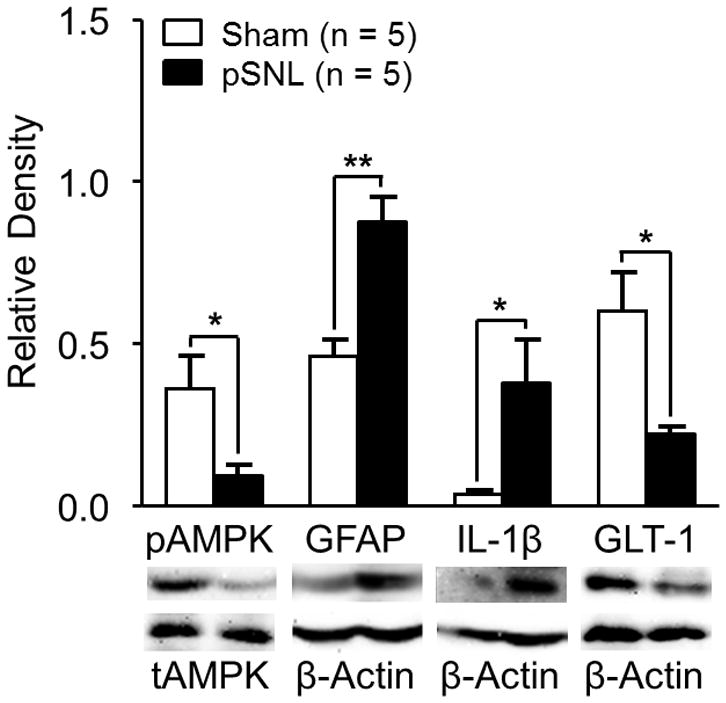
Ten days after nerve injury, protein expressions of phosphorylated adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α (pAMPK) and glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) in the spinal dorsal horn ipsilateral to the injury site are suppressed whereas glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) are increased. Bar graphs show the mean (+ SEM) ratio of pAMPKα/total AMPKα (tAMPK) as well as the mean (+ SEM) relative density of GFAP, IL-1β, and GLT-1 to β-Actin in the spinal dorsal horn of partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL) and Sham-operated rats. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
