Figure 5.
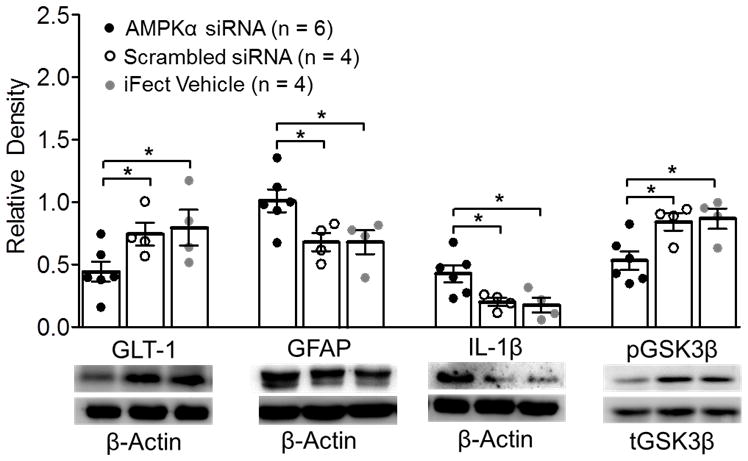
Spinal genetic knockdown of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) decreased glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) protein expression and increased glial fibrillary acid protein promoter (GFAP) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) protein expression, and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) activity in naïve rats. Bar graphs show the mean (± SEM) relative density of GLT-1, GFAP, and IL-1β to β-Actin and phosphorylated GSK3β (pGSK3β) to tGSK3β in the spinal dorsal horn of AMPKα small interfering RNA (siRNA), Scrambled siRNA, or the iFect Vehicle treated rats. Data obtained from individual animals are shown in the scatter plot. Samples of each molecule protein expression in each group are shown. * p < 0.05
