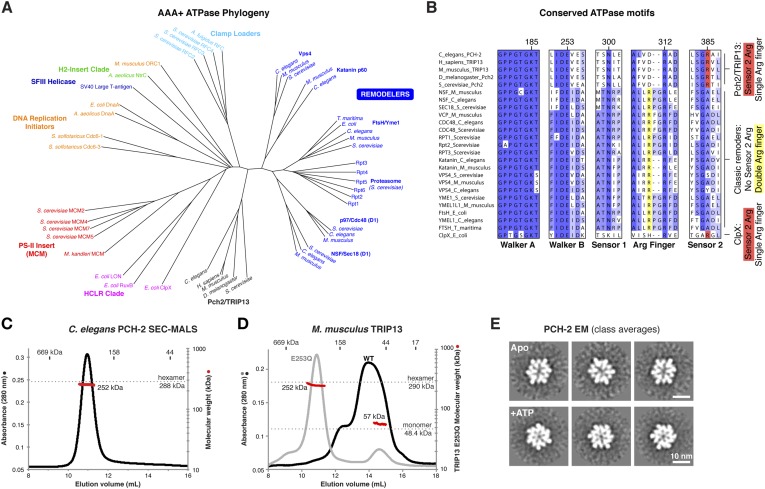
Figure 1. PCH-2/TRIP13 is a distinct class of hexmeric AAA+ ATPase.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of selected AAA+ ATPases, colored by clade (Erzberger and Berger, 2006). (B) Conserved AAA+ sequence motifs in Pch2/TRIP13, the ‘classic remodelers’, and E. coli ClpX. Pch2/TRIP13 and ClpX lack the first of two conserved arginine residues in the Arg finger region (yellow), and possess a Sensor 2 arginine (R385, red), which the classic remodelers lack. (C) Size-exclusion chromatography coupled to multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) analysis of C. elegans PCH-2 in the absence of nucleotides. Hexamer molecular weight = 288.1 kDa; measured molecular weight = 252 kDa (red line). (D) SEC-MALS analysis of M. musculus TRIP13 in the absence of nucleotides. The wild-type protein (black) adopts a mixture of oligomeric states from monomer to hexamer, consistent with findings from S. cerevisiae Pch2 (Chen et al., 2014). The proportion of higher-molecular weight oligomers increases upon the addition of ATP or non-hydrolyzable analogs (not shown). The ATP hydrolysis-defective TRIP13E253Q mutant (gray, molecular weight measurements red) is predominantly hexameric both in the presence (shown) and absence of ATP. Molecular weight measurements by SEC-MALS (red) are shown for TRIP13E253Q; WT measurements (not shown) are consistent. (E) Selected negative-stain EM class averages of C. elegans PCH-2 without added nucleotides (Apo) or with added ATP. For example raw images, see Figure 1—figure supplement 1.