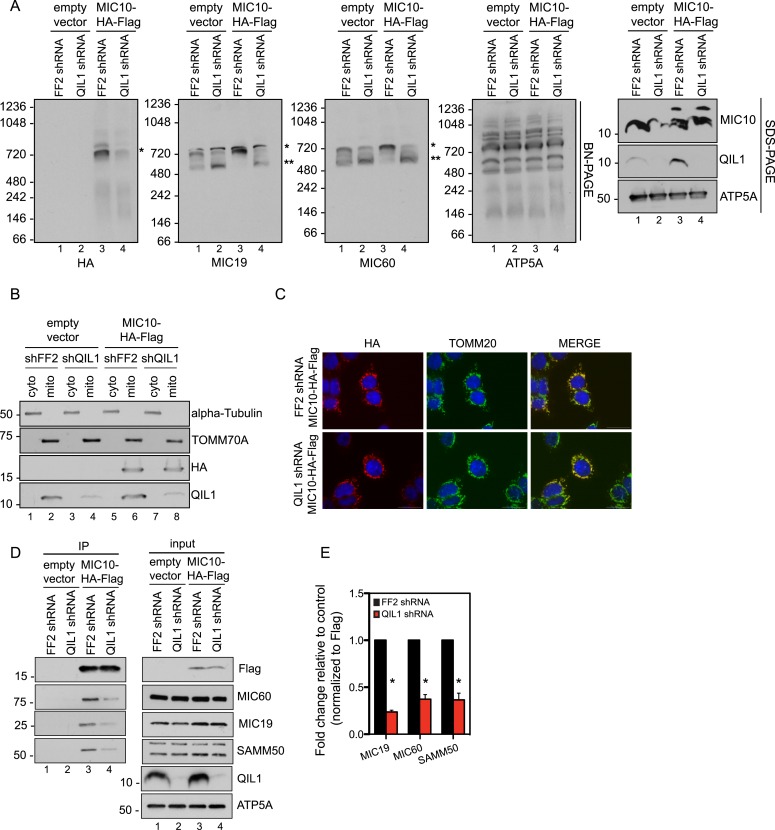
Figure 7. QIL1 is required for the binding of MIC10 to the MICOS complex.
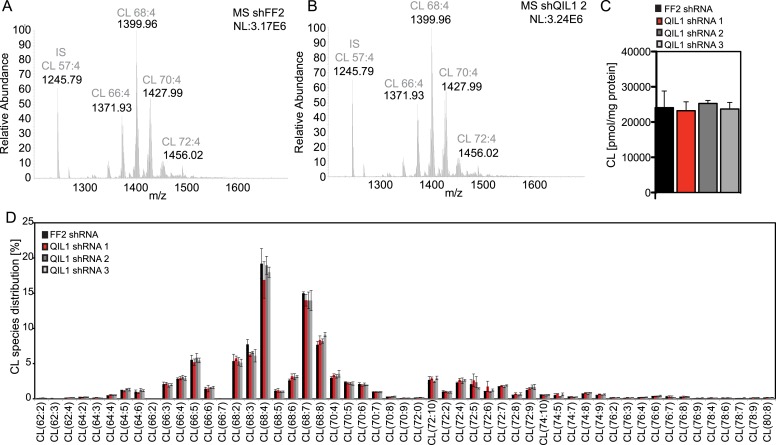
(A) BN-PAGE followed by immunotransfer to nitrocellulose membranes. Incorporation of C-terminally tagged MIC10 into the mature ∼700 kDa MICOS complex (asterisk) was decreased in cells expressing QIL1 shRNA compared to those expressing FF2 shRNA. (B) Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial fractions were separated in lysates obtained from HCT116 cells stably expressing FF2 or QIL1 shRNA and transiently expressing empty vector or C-terminally tagged MIC10. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of the subcellular localization of C-terminally tagged MIC10. Bars, 20 µm. (D) C-terminally tagged MIC10 was transiently expressed in HCT116 cell lines expressing FF2 shRNA or QIL1 shRNA and immunopurified from mitochondrial lysates. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect interaction with other MICOS subunits. (E) Densitometry analysis was performed using ImageJ. Figure 7—figure supplement 1 shows the analysis of cardiolipin content and species distribution by LC-MS/MS in mitochondria obtained from cells stably expressing FF2 or 3 different shRNAs targeting QIL1.