Figure 3.
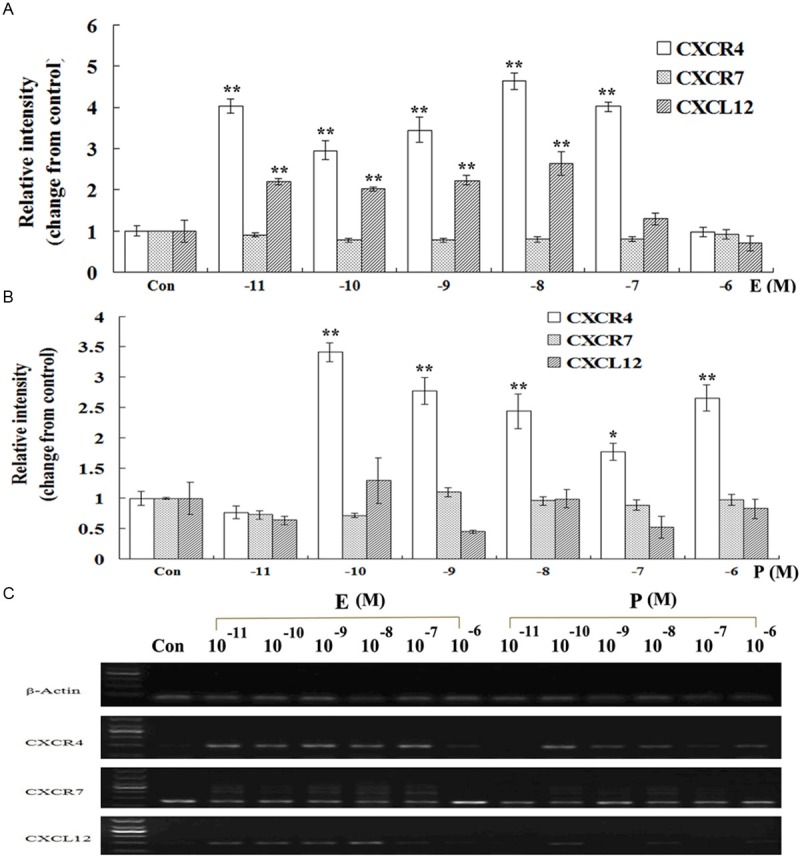
Effects of estrogen and progesterone on CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 mRNA expression in human ESCs. ESCs in mid-log growth were starved with DMEM/F12 for 12 h, then treated with vehicle (DMEM/F12 with 2% stripped FCS), estrogen (10-11-10-6 M) or progesterone (10-11-10-6 M) for 24 h. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCR) were performed to detect the effects of different concentration of steroid hormones on mRNA expression of CXCL12 (155 bp), CXCR4 (194 bp) and CXCR7 (164 bp) genes. The intensity of CXCL12, CXCR4 or CXCR7 gene was equal to the ratio of the absorbance of the target gene to that of the actin. Then the relative expression level of the target gene was changed from the corresponding control. A: Modulation of estrogen on CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 mRNA expression in ESCs. B: Modulation of progesterone on CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 mRNA expression in ESCs. C: One of the representative pictures for RT-PCR. Error bars depict the standard error of the mean. Compared with the control, *P < 0.01; **P < 0.05.
