Figure 1.
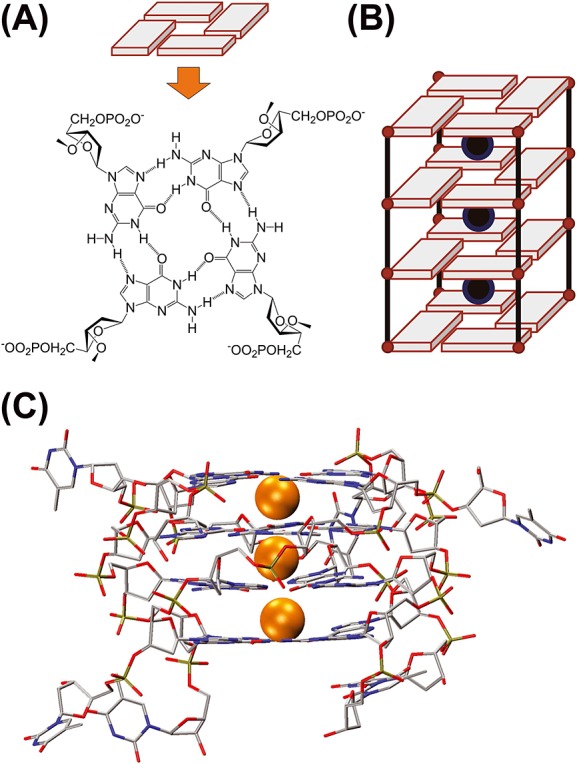
What is a G-quadruplex? (A) Four guanines forming a G-quartet via Hoogsteen H-bonds, involving N1-O6 and N2-N7 atoms. (B) Sequences containing consecutive guanines form G-quartets core stabilized by the coordination of monovalent cations in-between G-quartets. (C) 3-D crystal structure of the DNA G-quadruplex [dTGGGGT]4; cations shown as orange spheres; PDB reference 352D.[11]
