Figure 2.
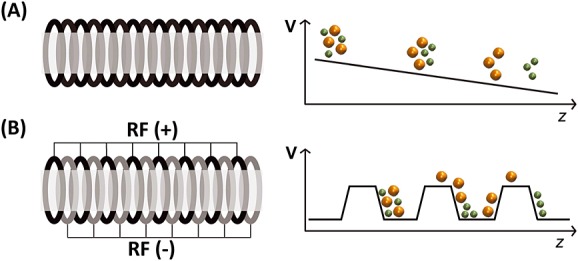
Main difference between (A) drift tube ion mobility spectrometry (DTIMS) and (B) traveling wave IMS (TWIMS). High mobility ions are in green and low mobility ions are in orange. (A) In DTIMS, a constant and homogeneous potential gradient is applied along the tube. (B) In TWIMS, the ions are confined by a radio frequency (RF) applied to a stacked ring ion guide. In addition, a direct current voltage wave is traveling to the exit (T-wave). Ions of higher mobility are picked up more easily by the waves, whereas larger ions are subjected to larger friction with the gas and slip more often behind the waves and therefore take longer to exit the mobility cell.
