Fig. 1.
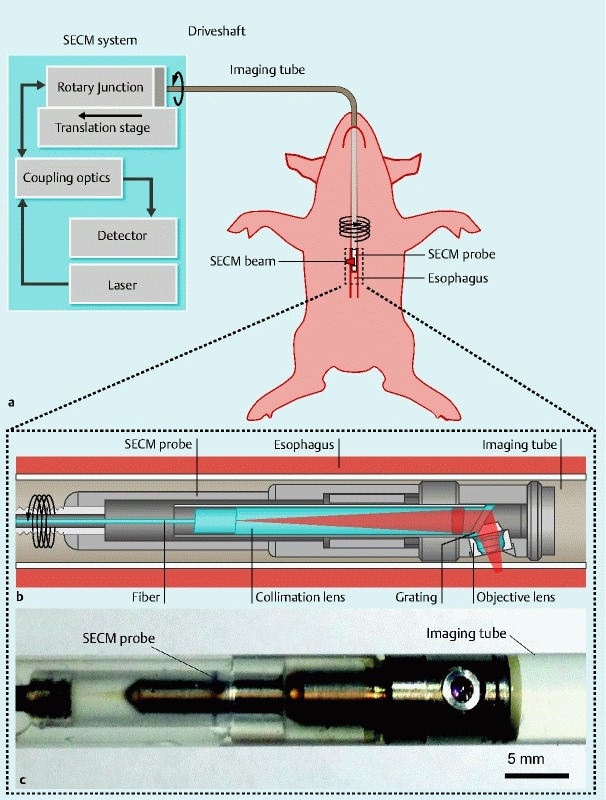
Schematics and photo of the SECM endoscopic imaging setup. a Overview of the SECM endoscopic imaging setup. An SECM endoscopic probe is inserted into an imaging tube, which is a transparent semi-flexible plastic tube. The imaging tube is introduced to the esophagus transorally. A SECM beam is focused into the esophageal tissue. While SECM images are continuously acquired, the SECM probe is helically scanned by a rotary junction and translation stage to image a large area of the esophagus. b Detailed schematic of the SECM probe optics. In the probe optics, light from the fiber is collimated by a collimation lens and diffracted by a grating. The diffracted light is focused by an objective lens (water immersion; numerical aperture = 0.5) into a 280-µm-long line. c Photo of the SECM optical probe inside the imaging tube. The diameter of the probe is 5.9 mm, and the rigid length is 30 mm. The outer diameter of the imaging tube is 7.0 mm.
