Figure 2. CRP levels are associated with increased fear-potentiated startle.
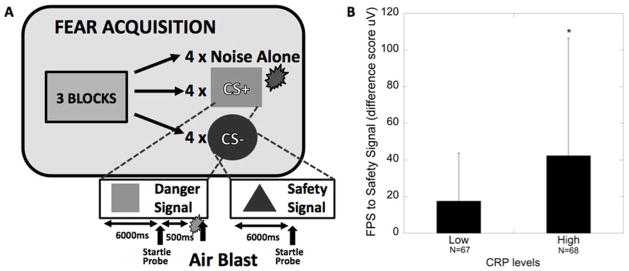
(A) Diagram of the fear-potentiated startle experiment; CS+=reinforced conditioned stimulus (danger signal), CS−=non-reinforced conditioned stimulus (safety signal); (B) Mean ± SD fear-potentiated startle (FPS) to the safety signal (CS-) in traumatized individuals with low and high levels of CRP (n=135).
