Figure 1.
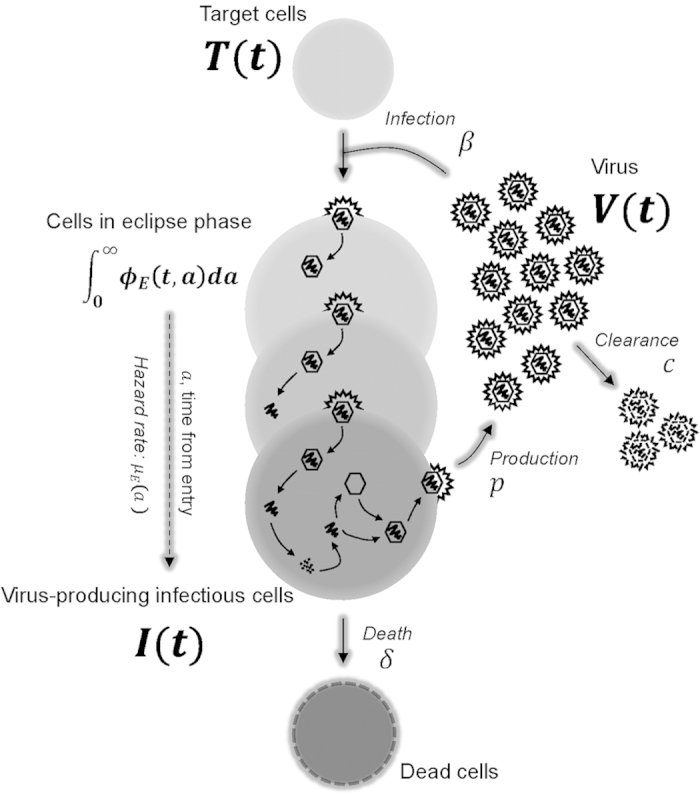
A schematic representation of the mathematical model. After a virion, 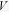 , successfully enters and infects a susceptible target cell,
, successfully enters and infects a susceptible target cell,  , at infection rate,
, at infection rate, 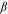 , the newly infected cell progresses through different stages of cell populations,
, the newly infected cell progresses through different stages of cell populations, 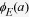 , which are structured according to the time elapsed,
, which are structured according to the time elapsed,  , since virus entry. Each of these stages has a corresponding age-dependent hazard rate,
, since virus entry. Each of these stages has a corresponding age-dependent hazard rate, 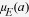 , for the probability that the newly infected cell in the eclipse phase transitions to the infectious state (i.e., becomes infectious,
, for the probability that the newly infected cell in the eclipse phase transitions to the infectious state (i.e., becomes infectious,  ) and begins virus production. An infectious, virus-producing cell,
) and begins virus production. An infectious, virus-producing cell,  , produces progeny virions at constant rate
, produces progeny virions at constant rate 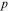 , and dies at rate
, and dies at rate  . The virions are cleared at rate
. The virions are cleared at rate  .
.
