Figure 7.
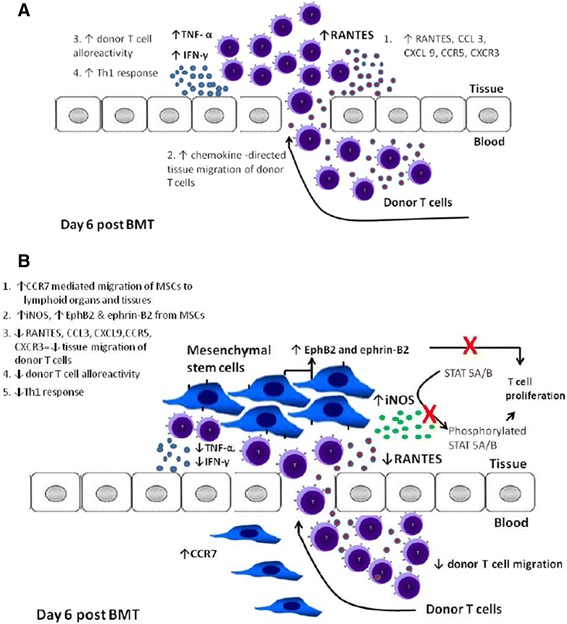
Immunosuppressive mechanisms of hMSCS in GVHD mouse models. (A) In the absence of hMSCs, upregulation of chemokine receptors and ligands causes migration of donor T cells to the target tissues of GVHD causing increased T cell alloreactivity and Th1 response. (B) With hMSC treatment, CCR7 increases migration of hMSCs to lymphoid organs and target tissues, then hMSCs produce soluble mediators (iNOS) causing immunosuppression. These soluble mediators suppress ligands CCL3, RANTES and CXCL9 and corresponding receptors CCR5 and CXCR3 with resultant decresased migration of donor T cells to the target tissues. This subsequently results to decreased TNF-α and IFN- γ. iNOS also suppresses phosphorylation of STAT 5A/B proteins that regulates T cell proliferation. EphB2 and ephrin-B2 which are specifically found in hMSCs also binds with T cells and suppress their proliferation.
