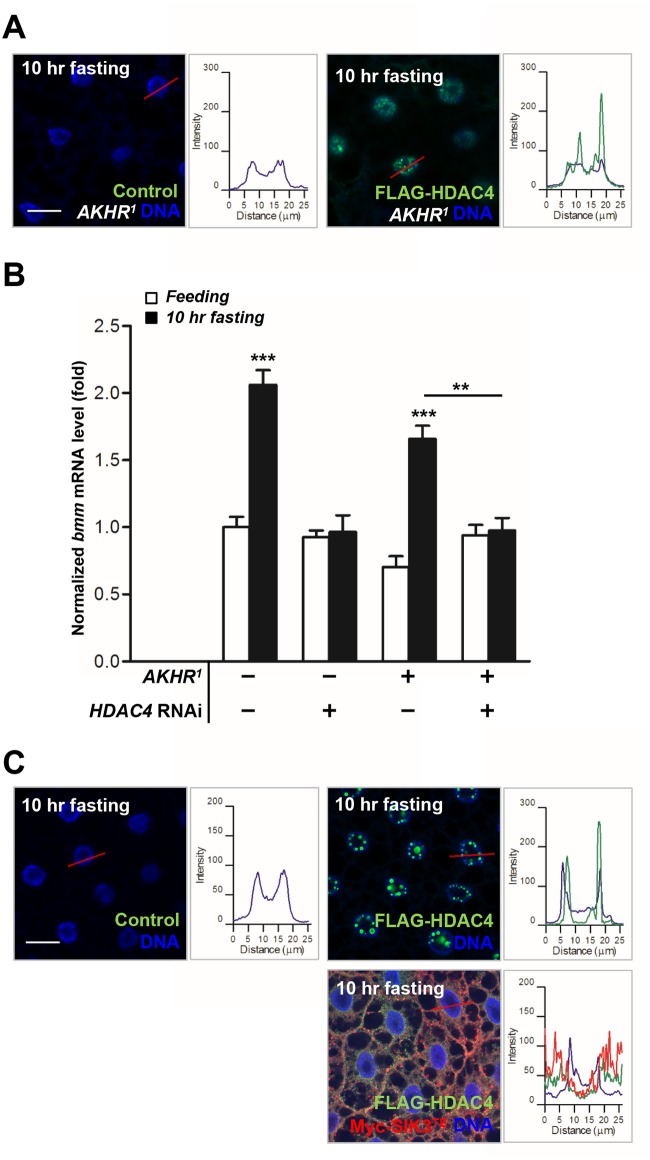
Fig 5. HDAC4 accumulated in the nuclei of the fat body cells in AKHR mutants under prolonged fasting.
(A) Immunohistochemical analyses of HDAC4 (anti-FLAG antibody, green) in AKHR mutant (AKHR 1) L3 larvae in 10 hr fasting condition as denoted in figures. Cell nuclei were stained by Hoechst 33258 (blue). Genotypes are as follows: Control (FB-Gal4,AKHR 1/AKHR 1) and FLAG-HDAC4,AKHR1 (FB-Gal4,AKHR 1/UAS-HDAC4,AKHR 1). The graphs showed the staining intensity profile for each antibody along the red lines. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Effects of the fat body-specific knockdown of HDAC4 (HDAC4 RNAi) on bmm gene expression in AKHR mutant adult flies (AKHR 1) in 10 hr fasting condition. Genotypes are as follows: Control (FB-Gal4/+), HDAC4 RNAi (FB-Gal4/+;UAS-HDAC4 RNAi/+), AKHR1 (FB-Gal4,AKHR 1/AKHR 1), and AKHR1,HDAC4 RNAi (FB-Gal4,AKHR 1/AKHR 1 ;UAS-HDAC4 RNAi/+). (C) Immunohistochemical analyses of HDAC4 (anti-FLAG antibody, green) in the fat body cells following expression of constitutively active (T196E) SIK3 in 10 hr fasting condition as denoted in figures. Genotypes are as follows: Control (FB-Gal4/+), FLAG-HDAC4 (FB-Gal4/UAS-HDAC4), and FLAG-HDAC4,SIK3TE (FB-Gal4/UAS-HDAC4;UAS-SIK3 T196E/+). The graphs showed the staining intensity profile for each antibody along the red lines. Scale bars, 20 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).