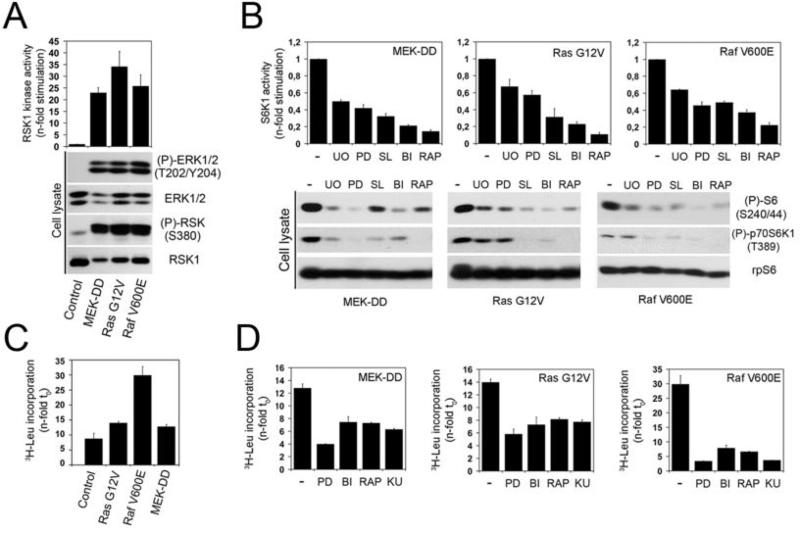
Fig. 1.
Oncogenic RAS and RAF promote mTORC1 signalling in a RSK-dependent manner. (A) HEK293 cells stably expressing constitutively-activated MEK1 (MEK-DD), Ras (G12V) or Raf (V600E) were serum-starved overnight, and analyzed for ERK and RSK phosphorylation by immunoblotting. Immunoprecipitated RSK1 kinase activity was assayed using GST-rpS6 as substrate, in the presence of γ[32P]ATP. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and the dried coomassie-stained gel autoradiographed. (B) HEK293 cells stably expressing constitutively-activated MEK1, Ras or Raf were serum-starved overnight, pre-treated with U0126 (U0), PD184352 (PD), SL0101 (SL), BI-D1870 (BI) or rapamycin (RAP) for 1h, prior to being harvested. Immunoprecipitated S6K1 kinase activity was assayed using GST-rpS6 as substrate, in the presence of γ[32P]ATP. The histogram shows quantifications of phosphorylated rpS6 from three independent experiments. Phosphorylation of endogenous rpS6 and S6K1, and total rpS6 protein level were monitored by immunoblotting. (C) Control and constitutively-activated cells were maintained in low-serum (2%) for 18 hr. Global protein synthesis was measured by adding 0.5 μCi/ml [3H]leucine to the medium for 6 hours. Histograms show radioactivity incorporation normalized to time 0. (D) As in (C), except that cells were treated with indicated inhibitors for 60 minutes prior to addition of 0.5 μCi/ml [3H]leucine to the medium.