Figure 1. Overview of methods to study the specificity of nucleases.
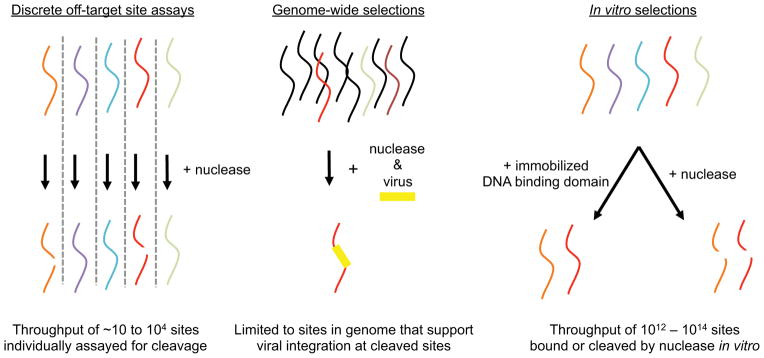
Potential substrate sequences of interest (colored strands) are subjected to nuclease cleavage to identify cleaved sequences (broken red and orange strands). In discrete off-target site assays, sequences are individually subjected to nuclease cleavage in a low- or high-throughput manner. In genome-wide selections, a few potential off-target sites are cleaved within predominantly uncleaved genomic DNA (black strands) and detected by viral integration. Using in vitro selection, many potential off-target sites in a vast DNA library are selected for binding or for their ability to be bound or cleaved site-specific nucleases in vitro.
