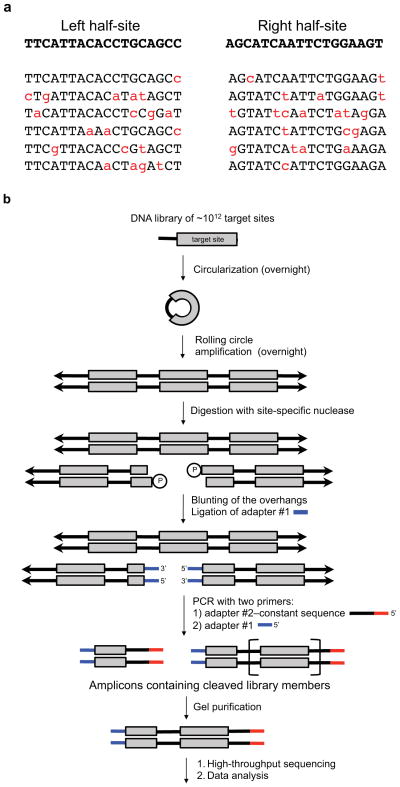
Figure 2. In vitro selection scheme for profiling the specificity of site-specific nucleases.
(a) Example sequences biased towards a target sequence for both the left- and right-half sites of TALEN targeting the human CCR5 gene. The on-target sequences are in bold and below are examples of variant sequences from minimally biased libraries. (b) A single-stranded library of DNA oligonucleotides containing partially randomized target sites (grey box) and constant region (thick black line) is circularized, then transformed into concatemeric repeats by rolling circle amplification. The concatemeric repeats of double stranded DNA (double arrows) target site variants are incubated in vitro with a site-specific nuclease of interest. The resulting and blunted ends are ligated to adapter #1. The ligation products are amplified by PCR using one primer consisting of adapter #1 and the other primer consisting of adapter #2–constant sequence, which anneals to the constant regions of the library. From the resulting ladder of amplicons containing 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, … repeats of a target site, amplicons corresponding to 1.5 target-sites in length are isolated by gel purification and subjected to high-throughput DNA sequencing and computational analysis.