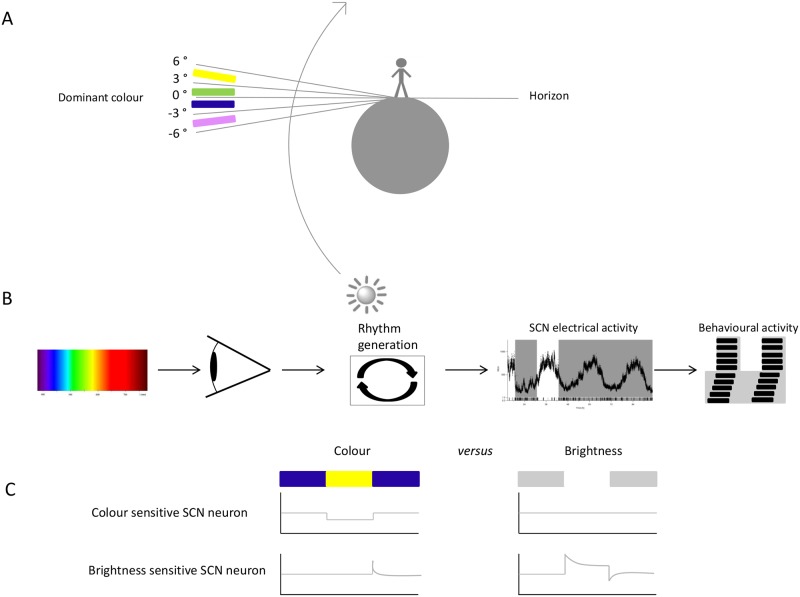
Fig 1. Colour detection by the circadian system.
Colour detection by the circadian system. (A) Spectral changes in light reaching the earth during twilight. At negative solar angles, short wavelength light is dominant, while at positive solar angles, long wavelength light is dominant. (B) Schematic overview of light signalling to the SCN resulting in entrainment to a light-dark cycle. Light is the main entraining signal that adjusts the endogenous period length to the day-night cycle. Electrical activity of SCN neurons is the main output signal of the SCN, which leads to temporal regulation of behavioural activity. (C) Schematic depiction of two types of light-responsive neurons observed in the SCN as shown by Walmsley and colleagues: the colour-sensitive neuron (upper traces) and the brightness-sensitive neurons (lower traces). Image credit: Hester van Diepen.