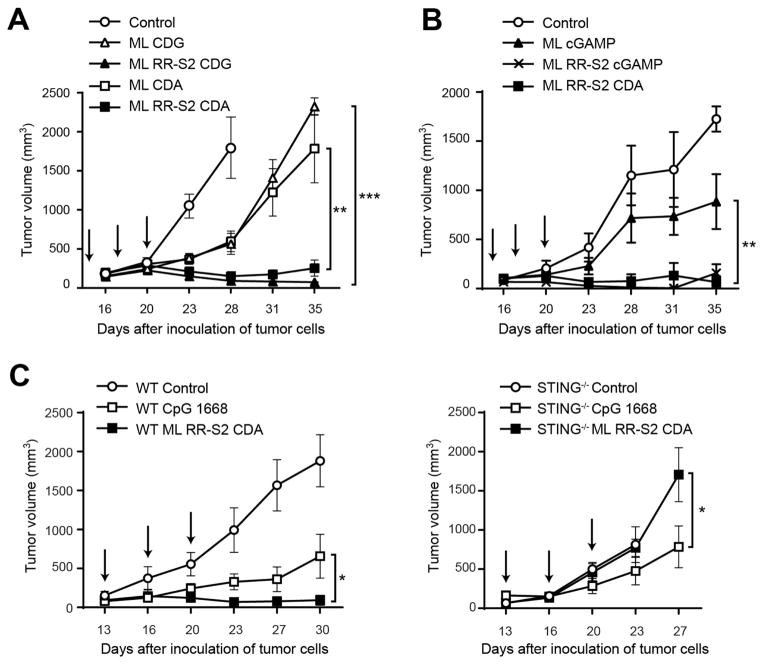
Figure 4. Synthetic CDN modifications significantly improve anti-tumor efficacy in established B16 tumors.
(A–B) WT C57BL/6 mice were inoculated with 5 × 104 B16.F10 cells in the left flank (n=8). When tumor volumes were 100 mm3 they received three 25 μg IT doses of ML CDA, ML CDG, ML RR-S2 CDG, or ML RR-S2 CDA or HBSS as control (A); or either three 50 μg doses of the endogenous cGAS product ML cGAMP, ML RR-S2 CDA, ML RR-S2 cGAMP or HBSS as control (n=8) (B). (C) WT C57BL/6 mice or STING−/− mice were treated with three IT doses of CDN ML RR-S2 CDA (50 μg), murine type B CpG ODN 1668 (50 μg) or HBSS vehicle control. Treatments were administered on the days indicated by the arrows and tumor measurements were taken twice weekly. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results are shown as mean tumor volume ± s.e.m. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. ns, not significant.