Fig. 3.
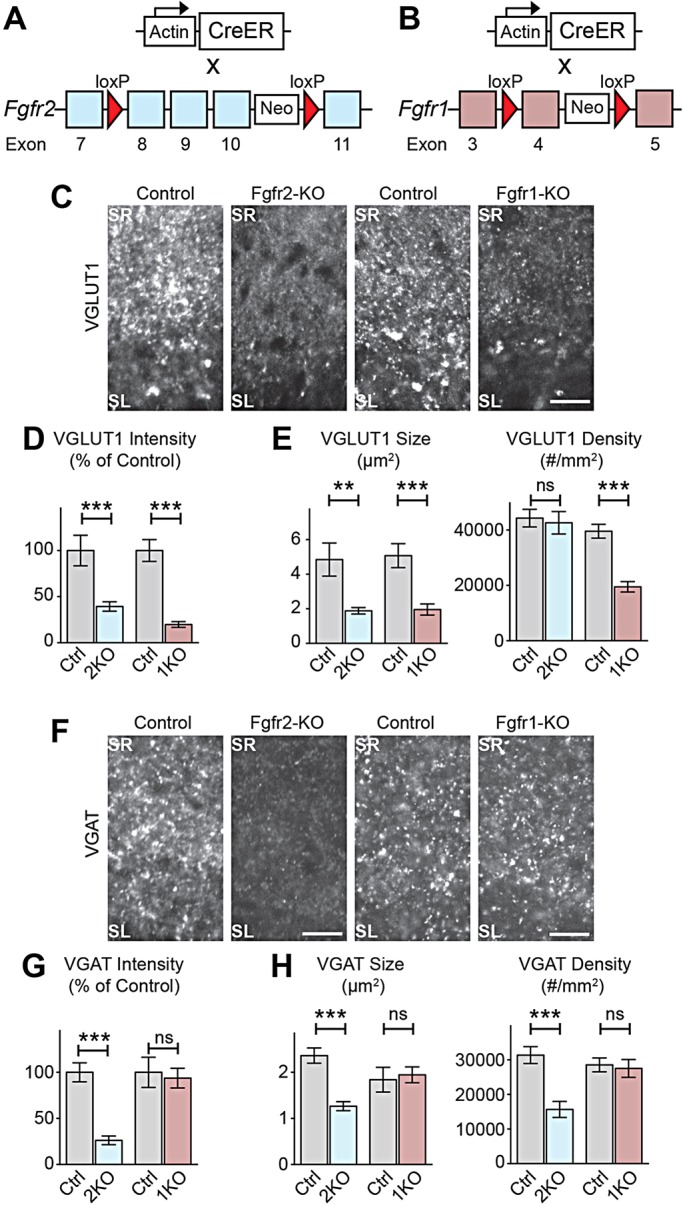
Temporally restricted loss of Fgfr2 and Fgfr1 during the synaptogenic period results in deficiencies in presynaptic differentiation in hippocampal CA3 in vivo. (A,B) Conditional Fgfr-KO strategy: mice carrying actin-promoter-driven CreER were crossed with Fgfr2flox/flox or Fgfr1flox/flox mice. Tamoxifen injection at P0 induced Fgfr deletion (Fgfr2-KO and Ffgr1-KO, respectively) postnatally. Controls: Cre-negative, tamoxifen-injected littermates. (C-E) Decreased excitatory presynaptic differentiation (VGLUT1 immunostaining) in CA3 of Fgfr2-KO and Fgfr1-KO at P8. (C) Representative images. (D) VGLUT1 intensity in SL, normalized to littermate controls. (E) VGLUT1 puncta size and density in SL [n=(sections, animals) 28, 4 Fgfr2-KO; 21, 3 Fgfr2-control; 24, 4 Fgfr1-KO; 24, 4 Fgfr1-control.] (F-H) Decreased inhibitory presynaptic differentiation (VGAT immunostaining) in CA3 of Fgfr2-KO but not Fgfr1-KO at P8. (F) Representative images. (G) VGAT intensity in SL, normalized to littermate controls. (H) VGAT puncta size and density in SL [n=(sections, animals) 34, 5 Fgfr2-KO; 35, 5 Fgfr2-control; 18, 3 Fgfr1-KO; 18, 3 Fgfr1-control.] Scale bars: 15 µm.
