Figure 1.
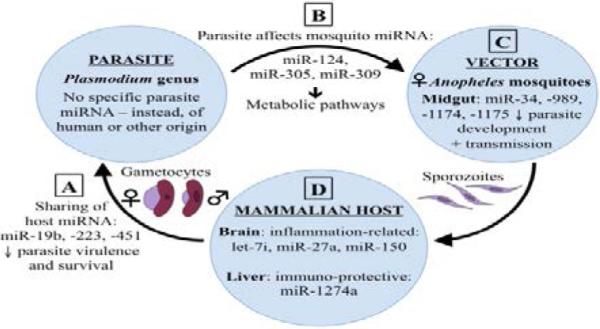
Dynamic interactions between the parasite, vector, and host in malarial infections. Cross-species interactions and regulation affects the transmission and pathogenesis of, and/or resistance to malaria infections. (A) Human miRNA (e.g. miR-19b, −223, and −451) [2] and (C) mosquito miRNA (e.g. miR-34, −989, −1174, and −1175)26 affect malaria parasite biology and survival. (B) Parasite miRNA (e.g. miR-124, −305, and −309)31 regulate metabolic pathways in Anopheles mosquitoes. (D) Host miRNA (e.g. let-7i, miR-27a, −150,51 −1274a42) regulate host gene expression.
