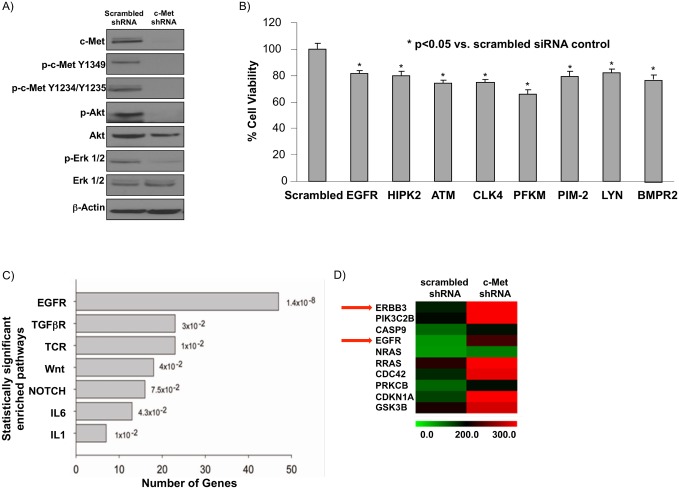
Fig 1. siRNA screening and microarray analysis of MHCC97-H liver cancer cell line stably transfected with c-Met shRNA reveals EGFR pathway as a putative survival pathway in HCC.
A) c-Met shRNA was stably transfected into the MHCC97-H cell line, which has constitutive c-Met activity. After puromycin selection, immunoblot determined c-Met knockdown in a c-Met+ HCC cell line suppresses downstream signaling (c-Met, Akt, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation) compared to MHCC97-H cells stably expressing a scrambled shRNA. B) An XTT assay was performed to confirm the eight targets from the siRNA screen that had the greatest effect on cell viability in MHCC97-H c-Met KD cells. 10 nM siRNA and 0.2 ul RNAiMAX were used to transfect MHCC97-H c-Met KD cells and cell viability was determined at 48 hours post transfection. C) Ingenuity pathway analysis was conducted to compare microarray gene expression between MHCC97-H c-Met knockdown (KD) cells and MHCC97-H cells stably expressing a scrambled shRNA. The top seven enriched pathways are shown. D) A heatmap of the subset of the EGFR pathway gene set that is differentially expressed by microarray (Illumina human gene chip). A statistically significant (p <0.05) 1.4-fold or greater change in expression between c-Met shRNA and scrambled shRNA cell lines was considered differentially expressed.