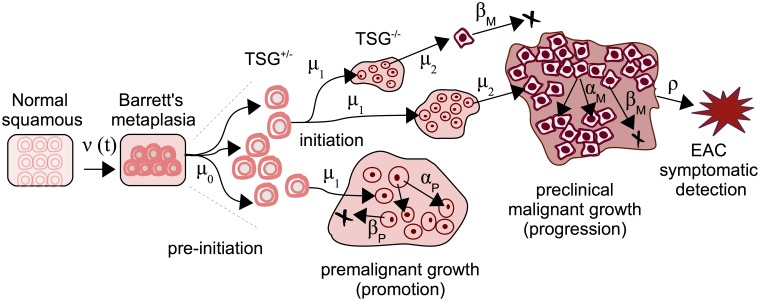
Fig 2. The multistage-clonal expansion model for EAC (MSCE-EAC) cell module.
Normal squamous epithelium may transform to BE with an exponentially distributed onset time with rate ν(t), followed by a ‘two-hit’ tumor initiation process with Poisson initiation rates μ 0, μ 1, which leads to the stochastic appearance of premalignant progenitor cells in the tissue. Premalignant cells undergo a first clonal expansion described by a birth-death-migration process with cell division rate α P, cell death-or-differentiation rate β P, and malignant transformation rate μ 2. Malignant cells, in turn, undergo a second clonal expansion by a birth-death-detection process with cell division and death rates α M and β M, respectively, allowing for stochastic growth and possibly extinction of the malignant tumor. Clinical detection occurs through a size-based detection process with parameter ρ. TSG, tumor suppressor gene.