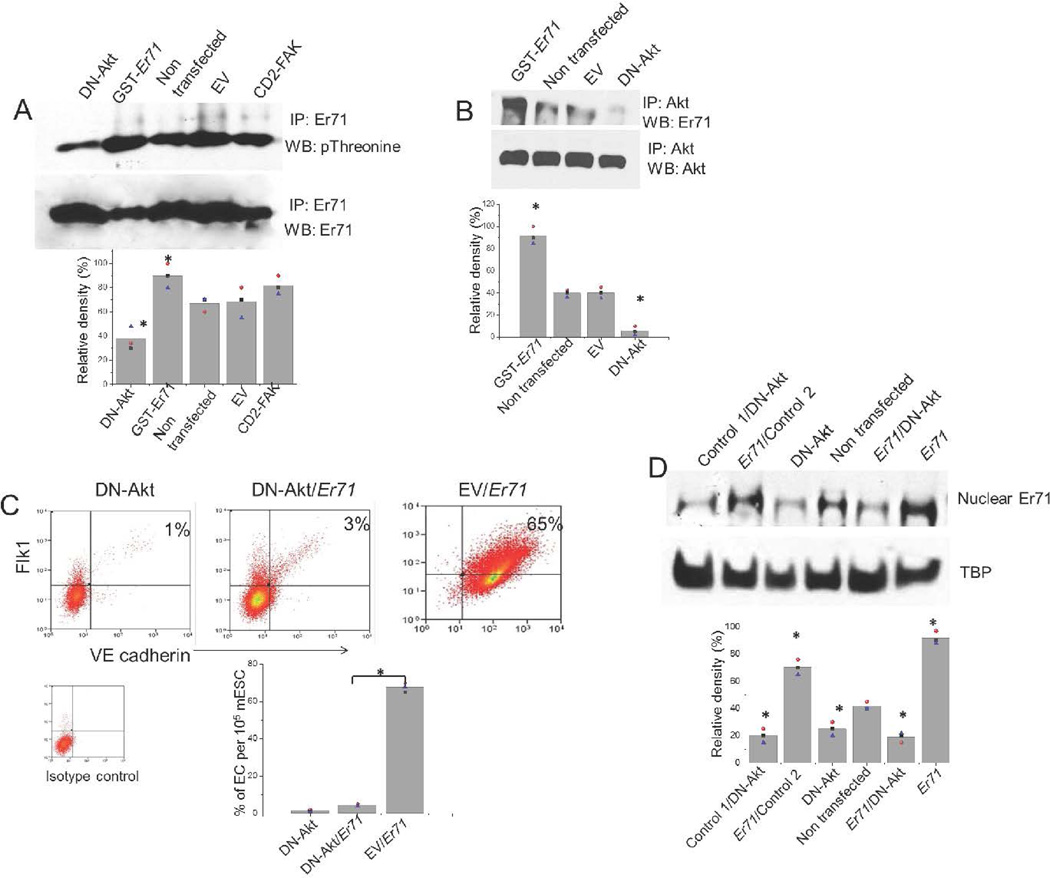
Figure 5. Akt mediates Er71 phosphorylation and induction of EC lineage transition.
(A) Akt regulates Er71 phosphorylation. mESCs transfected with DN-Akt or empty vector (EV) were exposed to mesodermal differentiation conditions. As positive controls we used mESCs transfected with constitutively-active CD2-FAK or mESCs transfected with GST-Er71 construct. At 15 min after exposure to VEGF165 containing media, the cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Er71, and analyzed by indicated antibody. Error bars, mean ± S.E.M., * P<0.05 for comparisons between experimental groups vs. controls, n=3.
(B) Activated Akt associates with Er71. mESCs transfected with DN-Akt, empty vector (EV) or GST-Er71 were exposed to VEGF165 containing differentiation media for 30min, cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Akt antibody and analyzed by WB with anti-Er71 antibody. Error bars, mean ± S.E.M., * P<0.05 for comparisons between experimental groups vs. controls, n=3.
(C) mESCs were transfected with DN-Akt alone or combined with GST-Er71 or DN-Akt empty vector (EV) combined with GST-Er71 and were exposed to differentiation conditions as per our standard protocol. After 6 days, cell surface expression of Flk1 and VE-cadherin (double positive) was examined by flow cytometry. Bar graph shows quantitation of Flk1+/VE-cadherin+ ECs under the 3 experimental conditions. Error bars, mean ± S.E.M., * P<0.05 vs indicated conditions, n=3.
(D) Akt is required for Er71 localization to nuclear compartment during mESCs differentiation into ECs. mESCs were transfected with DN-Akt, GST-Er71 or both, and were exposed to differentiation conditions as above. Controls were transfected with GST-empty vector (indicated as Control 1) and DN-Akt-empty vector (indicated as Control 2). At 1hr after exposure to VEGF165 in the differentiation media, cells were solubilized and the nuclear fraction used for WB against Er71. Error bars, mean ± S.E.M., * P<0.05 for comparisons between experimental groups vs. controls, n=3.