Figure 3. The interaction between MVBs and LDs is regulated by active Rab7.
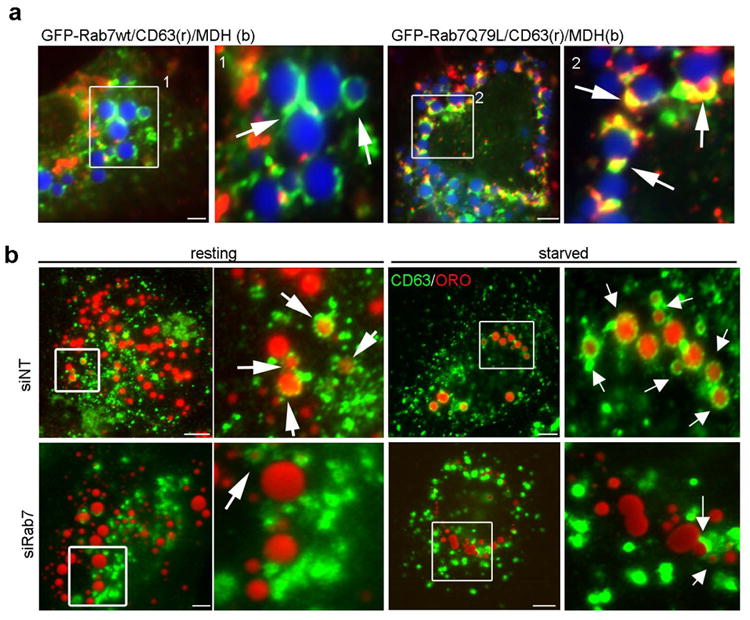
(a) IF images of Hep3B cells expressing GFP-Rab7-wt or the active – Q67L mutant loaded with oleate overnight. LDs were stained with MDH (blue) while MVBs were identified using an antibody specific to CD63 (red). In cells expressing wt Rab7, few LD-MVB interactions were observed whereas a substantial increase in the association between these compartments was observed in cells expressing the active Rab7-Q67L mutant. (b) MVB–LD association increases upon starvation and is inhibited by Rab7 depletion. Hep3B cells treated with siNT or siRab7 were loaded with oleate 24 h post transfection and then starved for 24 h in low serum medium. LDs were visualized using ORO. In control cells, punctate CD63-positive MVBs exhibit physical interactions with LDs that are markedly increased upon starvation (arrows). In contrast, CD63-labeled MVBs appear enlarged and aggregated with only limited LD interactions in Rab7 depleted cells under either resting or starved conditions. Scale bars = 5 μm.
