Figure 7. Rab7 mediates LD breakdown by recruiting degradative compartments: a working model.
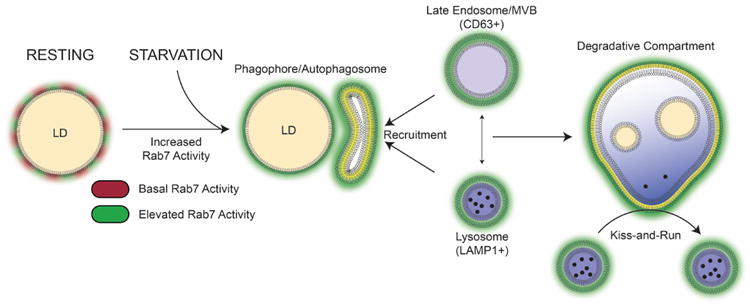
Under control conditions, LD-associated Rab7 (red) is activated upon starvation (green) to recruit LC3-positve APs that are also enriched in the active GTPase. This process is the first step in the lipophagic breakdown of the LDs. In a second step, the APs fuse with Rab7-positive degradative compartments to form an autolysosome for lipid degradation. This process may occur either via the formation of an amphisome (AP-MVB intermediate) that in turn fuses with the lysosome or via direct fusion of the AP with the lysosome (similar to classic macroautophagy). The direct interaction between lysosomes and APs can also occur in a “kiss-and-run”-like fashion allowing constant sampling of the autophagic LDs that will eventually result in LD degradation as observed by a reduction in LD number and area. Thus, functional Rab7 is indispensable for proper lipophagy as it controls both the integrity of the degradative compartments and their fusion with the LDs.
