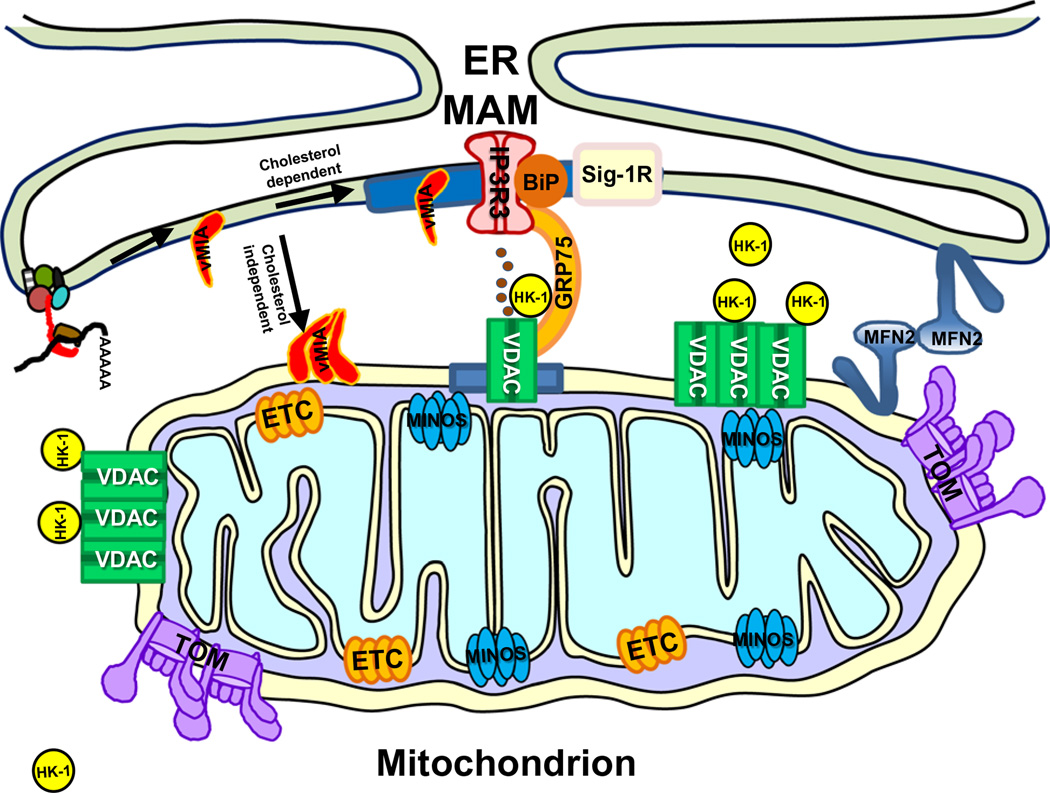
Fig. 2.
Schematic of vMIA trafficking and clustered distribution with respect to endogenous mitochondrial protein clusters. Shown is the translation of vMIA RNA at the ER membrane and its cholesterol dependent association with MAM lipid rafts (blue box), in close proximity with Sig-1R [5, 39]. MAM tether proteins (Mfn2) and components of the MAM calcium signaling complex, including IP3R3, its chaperone BiP, GRP75, and VDAC are shown. vMIA uses a cholesterol-independent mechanism to translocate to the OMM [5], where it is organized in clusters [93]. Other mitochondrial proteins including VDAC and associated hexokinase 1 (HK-1) [95, 96], and components of the TOM complex [94], electron transport chain (ETC) [95], as well as the MINOS complex [100] are also organized in clusters in mitochondrial membranes