Fig. 1.
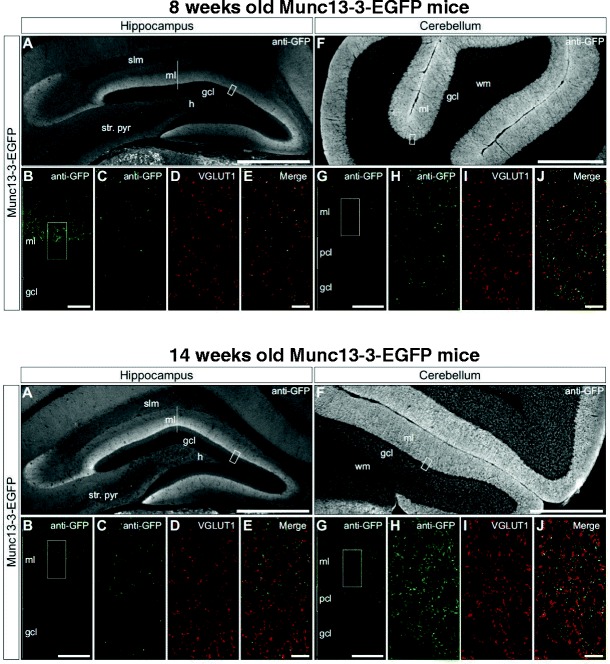
Immunolocalization of Munc13-3 in hippocampus and cerebellum. Upper row—8-week-old Munc13-3-EGFP mice. Lower row—14-week-old Munc13-3-EGFP mice. Munc13-3 immunoreactivity in the hippocampus (A–E) and cerebellum (F–J) is revealed by immunodetection of GFP in 8- and 14-week-old Munc13-3-EGFP mice. The expression pattern of the Munc13-3-EGFP signal is similar in both age groups. In the hippocampus, the pattern of GFP immunoreactivity is consistent with the expression of Munc13-3 in perforant path inputs to the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus and the stratum lacunosum-moleculare of the CA3 subregion. B, G Single-plane confocal micrographs of regions depicted by white boxes (A, F) illustrate that Munc13-3-EGFP signal is restricted primarily to the central and outer laminae of the dentate gyrus molecular layer in the hippocampus (B) and to granule cell and molecular layers in the cerebellum (G). C–E, H–J In the dentate gyrus (C–E) and the cerebellum (H–J), dual labeling confocal microscopy reveals frequent colocalization of Munc13-3-EGFP (C, H) and VGLUT1 (D, I) signals, as seen in the merged panels (E, J), indicating that Munc13-3 is primarily localized to glutamatergic presynaptic terminals. gcl granule cell layer, pcl Purkinje cell layer, ml molecular layer, h hilus, slm stratum lacunosum-moleculare, str. pyr stratum pyramidale, wm white matter. Scale bars: A, F, 500 μm; B, G, 20 μm; E, J, 5 μm
