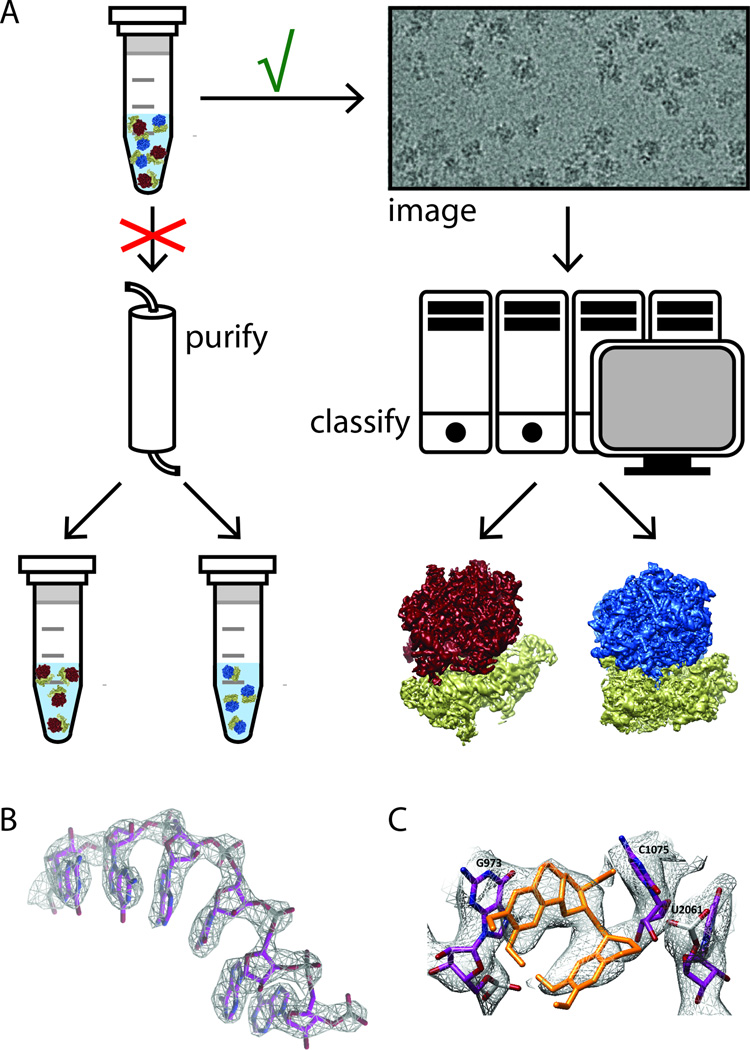
Figure 4. High-resolution cryo-EM structures from heterogeneous samples.
(A) To some extent, the classical approach in structural biology to study biochemically purified, homogeneous samples may be bypassed by cryo-EM image processing, where images of a mixture may be separated in the computer using powerful classification algorithms to obtain high-resolution structures for multiple components in the mixture. (B) Provided enough particles may be identified for each component, atomic-resolution maps may be generated for each of them. (C) Even small-molecule compounds may be built inside the high-resolution maps, in this case the eukaryotic translation inhibitor emetine is shown bound to the cytoplasmic ribosome from the P. falciparum parasite.